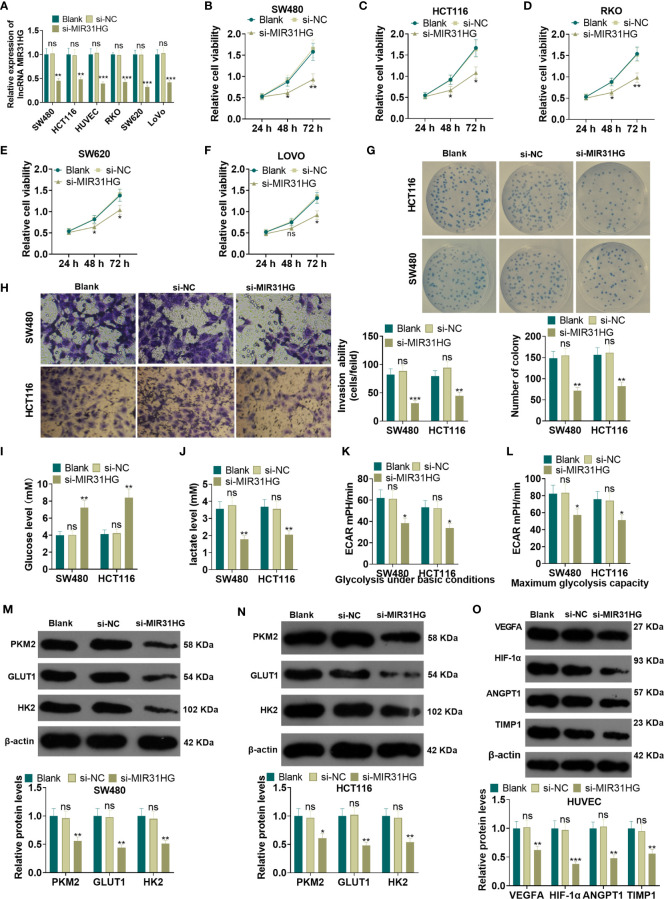
Figure 3.
Knocking down MIR31HG abated the proliferation and glycolysis of CRC cells and angiogenesis of endothelial cells. The MIR31HG knockdown model was constructed in CRC cell lines (Caco-2, RKO, SW480, SW620, LoVo and HCT116) and HUVEC cell lines. (A) The transfection validity was examined by qRT-PCR. (B–F) MTT assay was used to detect the proliferation of Caco-2, RKO, SW480, SW620, LoVo and HCT116 cells. (G) CRC cell proliferation wastested by colony formation assay. (H). Transwell assay were employed to evaluate CRC cell invasion. (I, J) The glucose and lactic acid production of CRC cells were measured using a glucose detection kit and lactic acid detection kit. (K, L) Glycolytic stress test was utilized to monitor the glycolytic level of CRC cells. (M, N) The expression of glycolysis-related proteins (PKM2, GLUT1, and HK2) in CRC cells was compared by WB. (O) Western blot was used for detecting the expression of angiogenesis markers (including VEGFA, ANGPT1, HIF-1α and TIMP1) in HUVECs with MIR31HG overexpression. NS p > 0.05 (vs. Blank group), *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.01 (vs. si-NC group). (n=3).