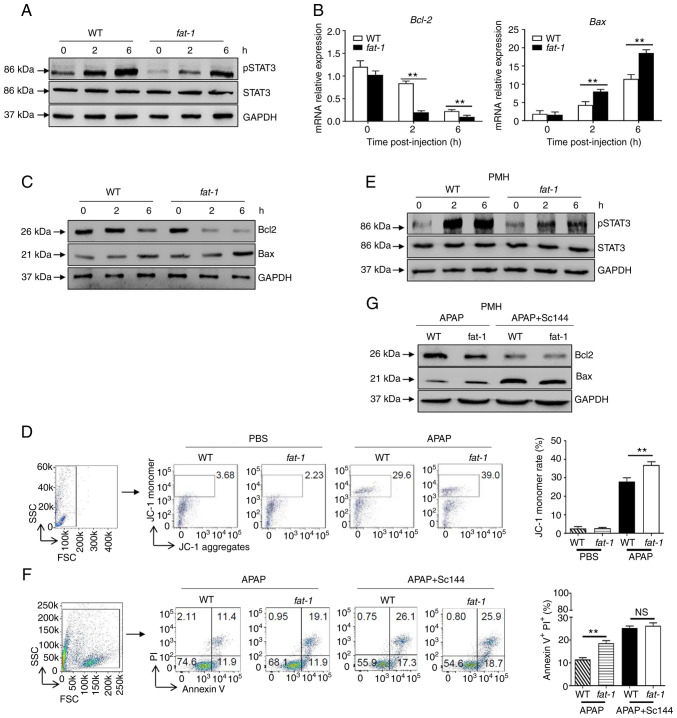
Figure 2.
N-3 PUFAs promote hepatocytes apoptosis through dephosphorylation of STAT3 signaling. (A-D) Hepatocytes were isolated from WT and fat-1 transgenic mice (n=5) at the indicated time after APAP (400 mg/kg) injection. (A) Protein levels of pSTAT3, STAT3 and GAPDH were determined by western blotting analysis. (B) The mRNA levels of Bcl-2 and Bax were measured by reverse transcription-quantitative PCR and expressed as a ratio to GAPDH. (C) The hepatic protein levels of Bcl-2, Bax and GAPDH were evaluated at different time points by western blotting analysis. (D) Mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) was detected in mouse hepatocytes by flow cytometry 6 h post-APAP injection. (E-G) Primary hepatocytes were isolated from WT and fat-1 mice (n=5) and were stimulated with 20 mM APAP in vitro. In some cases, cells were pretreated with 10 µM Sc144 for 2 h before APAP stimulation. (E) The levels of pSTAT3, STAT3 and GAPDH were detected by western blotting analysis. (F) Cellular apoptosis was measured by Annexin V-PI staining 24 h post-APAP treatment. (G) The protein levels of Bcl-2, Bax and GAPDH expression were determined by western blotting analysis 6 h post-APAP treatment. **P<0.01. NS, not significant; N-3 PUFAs, omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids; APAP, acetaminophen; WT, wild-type; p, phosphorylated.