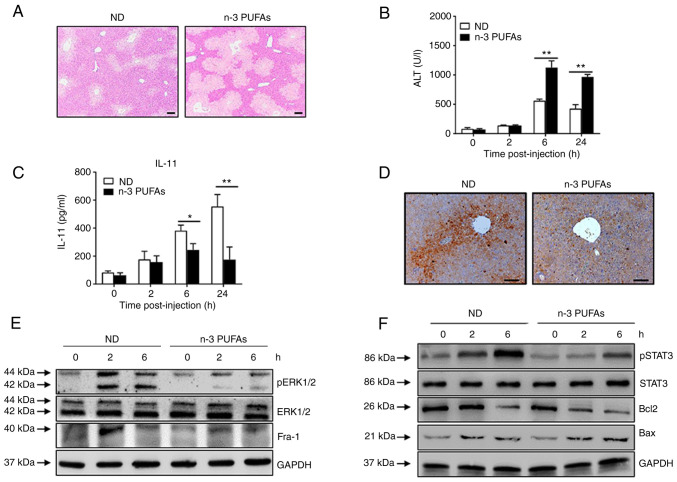
Figure 5.
Exogenous DHA aggravate APAP-induced liver damage through dephosphorylated ERK-mediated decreased IL-11 production. (A-D) An overdose of APAP (400 mg/kg) was intraperitoneally injected into WT mice fed with ND or n-3 PUFA-enriched diet (n=5). (A) Histological analysis of mouse livers was performed by hematoxylin & eosin staining. Scale bar, 100 µm. (B) Serum ALT activities at different time points were measured. (C) The serum level of IL-11 was determined at the indicated time points post-APAP injection. (D) The protein level of IL-11 in the liver tissues was detected by immunohistochemical staining 6 h post-APAP injection. Scale bar, 50 µm. (E and F) Hepatocytes were isolated from WT mice fed with ND or n-3 PUFA-enriched diet (n=5) at the indicated time post-400 mg/kg APAP administration. (E) The levels of pERK, ERK, Fra-1 and GAPDH were determined by western blotting analysis. (F) The protein levels of pSTAT3, STAT3, Bcl-2, BAX and GAPDH were detected by western blotting analysis. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. N-3 PUFAs, omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids; APAP, acetaminophen; WT, wild-type; ALP, alanine aminotransferase; Fra-1, Fos-like-1; p, phosphorylated; ND, normal diet.