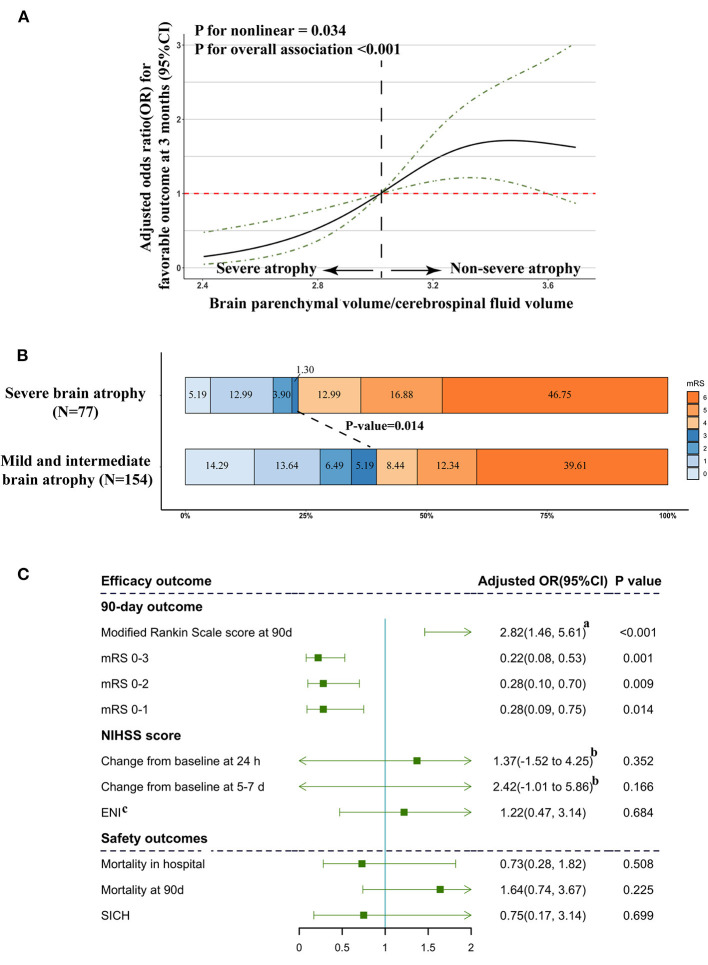
Figure 1.
Association of severe brain atrophy with clinical outcome. (A) Association of brain atrophy with favorable outcome (mRS ≤ 3) in a restricted cubic spline model. Brain atrophy was estimated by quantifying BPV/CFV. ORs, solid line; 95% CI, dashed lines. (B) Primary outcomes according to brain atrophy status. Distribution of modified Rankin Scale (mRS) scores at 3 months in patients treated with endovascular treatment. (C) Multivariable logistic regression analysis revealed the relationship between brain atrophy and efficacy outcome and safety outcome. Adjusted estimates of outcome were calculated using multiple regression, taking the following variables into account: age, sex, dyslipidemia, atrial fibrillation, baseline NIHSS score, baseline PC-ASPECTS, mTICI, PC-CS, and onset to recanalization time. (a) Common odds ratio; (b) β and 95% CI values were estimated from a multivariable linear regression model, which was adjusted by multiple regression, taking the following variables into account: age, sex, dyslipidemia, atrial fibrillation, baseline NIHSS score, baseline PC-ASPECTS, mTICI, PC-CS score, and onset to recanalization time. (c) ENI: early neurological improvement was estimated by a reduction of > 8 or return to 0 on NIHSS compared with baseline score at 24 h after EVT.