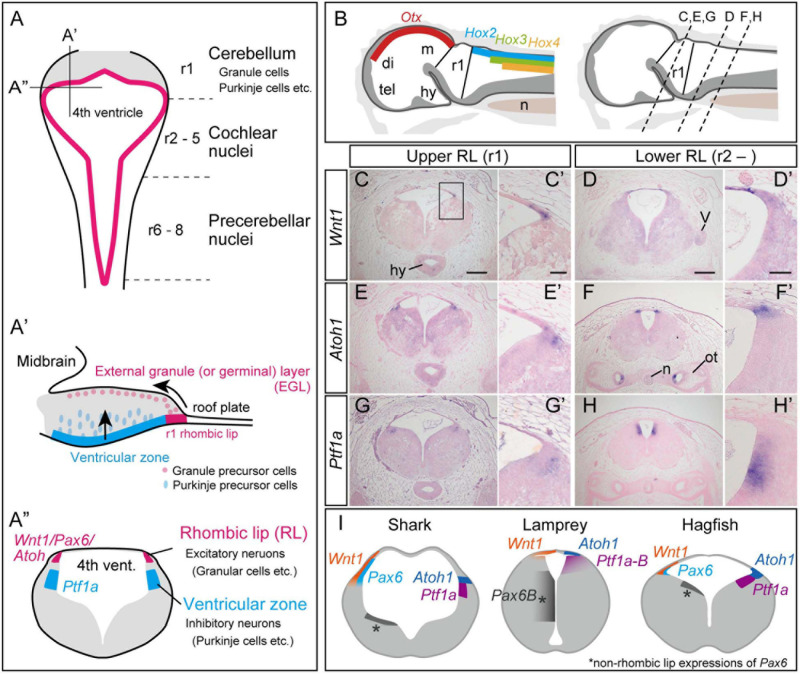
FIGURE 1.
Development of the cerebellum in mammals, based on Fujiyama et al., 2009 (A). (A) Dorsal view of the rhombomeres. The rhombomere 1 (r1) gives rise to the cerebellum, while r2–8 generates the cochlear nuclei and precerebellar nuclei. (A’) Sagittal view of the rhombomere 1. Granule precursor cells, generated in the r1 rhombic lip, migrate tangentially to form the external germinal layer (EGL). The Purkinje precursor cells originating from the ventricular zone secrete Shh, which is involved in the proliferation of the granule cells. The granule cells in EGL then migrate ventrally to form the granular layer. (A”) Transverse view of rhombomere 1 showing the rhombic lip as the source for excitatory neurons, and the ventricular zone where the inhibitory neurons arise. (B–H) Upper and lower rhombic lip gene expression patterns in the hagfish, E. burgeri. (B) Illustration of a sagittal section of the anterior part of a stage 53 embryo. (left) Rhombomere 1 (Upper rhombic lip) is identified as a negative region of both Otx and Hox genes (Oisi et al., 2013; Pascual-Anaya et al., 2018). (right) Anterior-posterior level of transverse sections shown in (C–H) are indicated in a sagittal illustration. (C–H) Section in situ hybridizations for hagfish Wnt1, Atoh1 and Ptf1a genes showing their expression patterns in r1 (C,E,G) and posterior to r1 (D,F,H). (C’–H’) Higher magnification images of the rhombic lip expression patterns shown in (C–H). (I) Comparison of the upper rhombic lip gene expression patterns in the shark (S. torazame), lamprey (L. camtschaticum), and hagfish (E. burgeri) based on Sugahara et al. (2017) and the present study. di, diencephalon; hy, hypothalamus; m, mesencephalon; n, notochord; ot, otic capsule; tel, telencephalon; r1, rhombomere 1; V, trigeminal nerve. Scale bars: 200 μm (C–H), 50 μm (C’–H’).