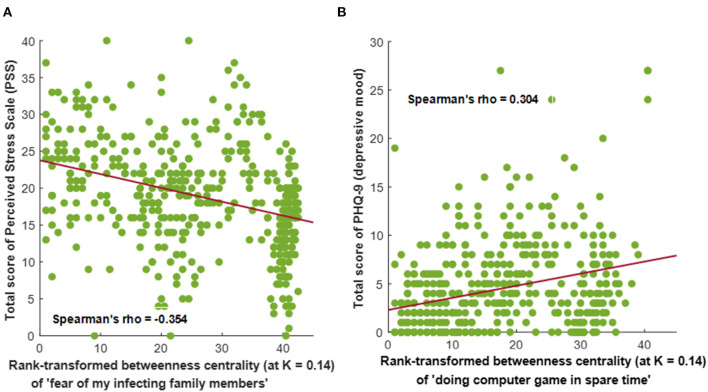
Figure 3.
Significant correlations between the intensity of perceived stress or depressive mood vs. rank-transformed betweenness centralities of personal attitudes or changes in lifestyle during the COVID-19 pandemic among Korean medical students (n = 454; statistical threshold of |Spearman's rho| > 0.3 and P < 0.001). Values of rank-transformed betweenness centrality were calculated from the intra-individual covariance networks (at network sparsity level of K = 0.14) containing the changes in lifestyle, personal attitudes, perceived stress, anxiety, and depressive mood. (A) Correlations between the total score of perceived stress scale (PSS) vs. rank-transformed betweenness centrality values of “personal attitude, fear of infecting my family members” (Spearman's rho = −0.354, P < 0.001). (B) Correlations between PHQ-9 (depressive mood) total score vs. rank-transformed betweenness centrality values of “engaging in computer games in spare time” (Spearman's rho = 0.304, P < 0.001).