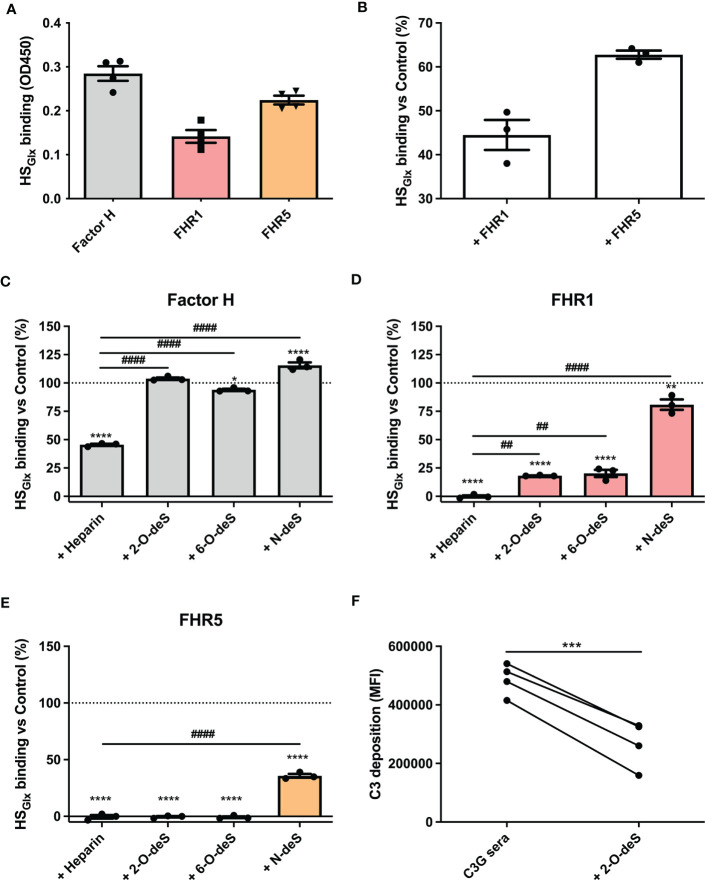
Figure 3.
O-desulfated heparins reduce FHR1 and FHR5 binding to purified glomerular endothelial glycocalyx-derived heparan sulfate (HS), without affecting FH binding. HS was purified from isolated glycocalyx from conditionally immortalized glomerular endothelial cells (HSGlx) and immobilized on microtiter plates. Binding of factor H (FH) and factor H-related proteins (FHRs) was measured using ELISA (n=4) (A). For competition assays, HSGlx was incubated with FHR1 or FHR5 before binding of FH was determined (n=3) (B). The contribution of specific sulfate modifications to HSGlx binding of FH (n=3) (C), FHR1 (n=3) (D) and FHR5 (n=3) (E) was evaluated by preincubating proteins with buffer (Control), heparin or 2-O-, 6-O- and N-desulfated (deS) heparin before addition to microtiter plates. To investigate potential therapeutic effects of 2-O-desulfated heparin in context of C3G patient sera (402H/H haplotype group with >1.5x increased C3 deposition compared to NHS), sera were supplemented with 50 µg/ml 2-O-desulfated heparin before addition to the cells (n=4) (F). (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001 vs Control; ##p < 0.01, ####p < 0.0001 vs Heparin; ***p<0.001 vs C3G sera.)