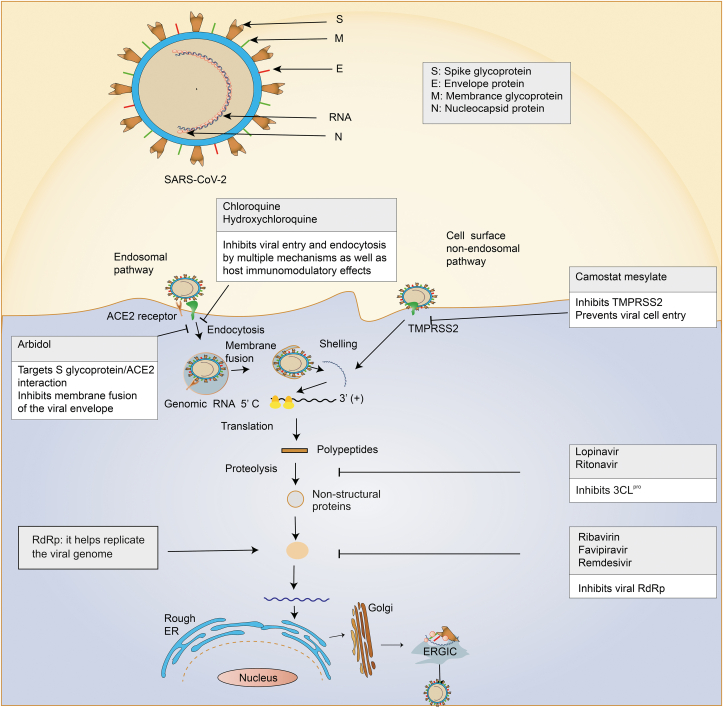
Fig. 1.
The mechanisms of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection and drug targets are reviewed. SARS-CoV-2 consists of RNA and four main structural proteins including spike (S), envelope (E), membrane (M), and nucleocapsid (N), which encodes several non-structural proteins, including 3C-like protease (3CLpro), RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), and papain-like protease (PLpro). Entry of SARS-CoV-2 into host cells includes both endosomal and non-endosomal pathways. The effect of anti-SARS-CoV-2 can be exerted by the inhibitors of corresponding target proteins. ACE2: angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; TMPRSS2: transmembrane serine protease 2; ER: endoplasmic reticulum.