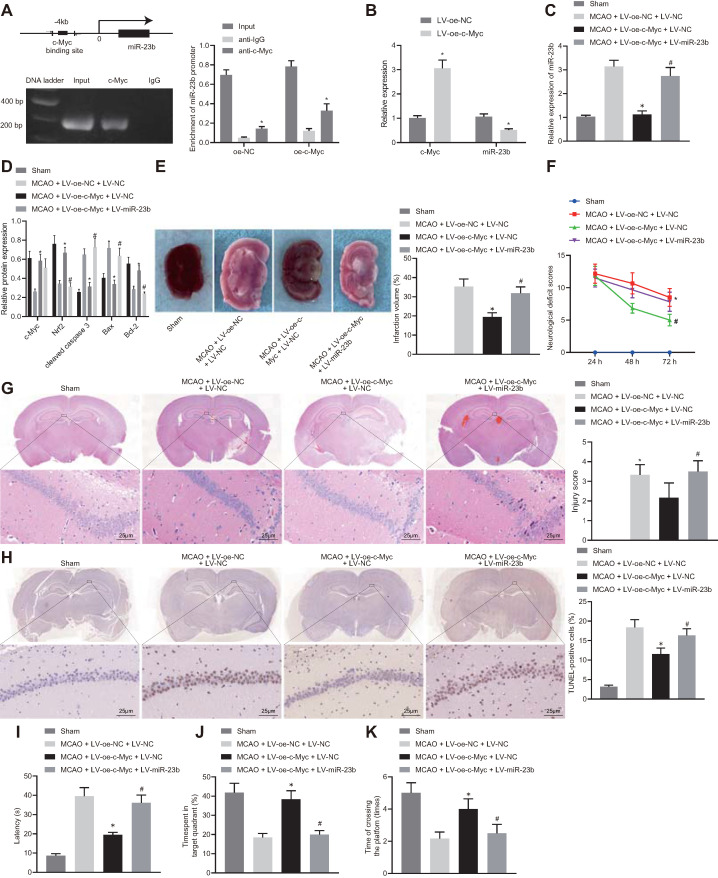
Figure 5.
c-Myc alleviates nerve injury in MCAO mice through regulating miR-23b/Nrf2 axis. A, The binding site of c-Myc in miR-23b promoter and enrichment of transcription factor c-Myc in miR-23b promoter detected by ChIP. B, miR-23b expression in mouse cerebral cortex neurons detected by RT-qPCR. C, miR-23b expression in mouse brain tissues detected by RT-qPCR. D, Protein expression of c-Myc, Nrf2, Bax, Bcl-2, and cleaved caspase-3 in mouse brain tissues by Western blot analysis. E, Area of brain infarction was detected by TTC staining. F, Neurological scores of mice in each group. G, HE (400 ×) staining of brain tissues. H, TUNEL (400 ×) staining of apoptosis of brain tissues. I, Latency of mice examined by Morris water maze test. J, Time of mice spent in target quadrant examined by Morris water maze test. K, Times of mice crossing the platform examined by Morris water maze test. * p < 0.05 vs. the anti-IgG, LV-oe-NC, or MCAO + LV-oe-NC + LV-NC group, # p < 0.05 vs. the MCAO + LV-oe-c-Myc + LV-NC group. Measurement data were expressed by mean ± standard deviation. Unpaired t test was performed for data comparison between two groups. One-way ANOVA was conducted for multi-group data comparison, followed by Tukey's post hoc test. Pairwise comparison of neurological scores in panel F was analyzed by non-parametric test Mann-Whitney test. n = 10.