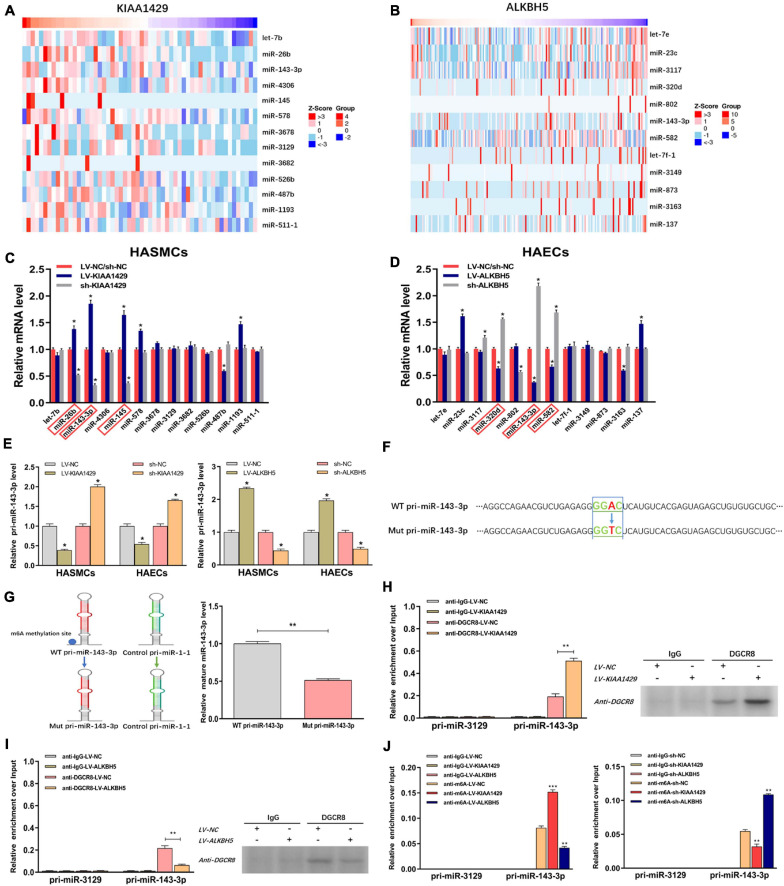
FIGURE 5.
KIAA1429 and ALKBH5 oppositely regulate the processing of miR-143-3p via m6A modification. (A,B) Through searching in the LinkedOmics database, we found 13 miRNAs positively associated in expression with KIAA1429 and 12 miRNAs negatively associated with ALKBH5. (C) The levels of miR-26b, miR-143-3p, and miR-145 increased when KIAA1429 was overexpressed and decreased when KIAA1429 was silenced. (D) The levels of miR-320d, miR-143-3p, and miR-582 were negatively regulated by ALKBH5. (E) The unprocessed pri-miRNA-143-3p was accumulated in KIAA1429-knockdown or ALKBH5-overexpression cells and significantly decreased in KIAA1429-overexpression or ALKBH5-silence cells. (F) In one reporter, the adenosine [A] of the RRACH m6A sequence motif located in the pri-miR-143-3p region outside the pre-miR-143-3p sequence was mutated to thymidine [T]. (G) The mutation of the RRACH m6A motif in pri-miR-143-3p significantly reduced its processing to the mature form. (H,I) The levels of pri-miR-143-3p bound to DGCR8 were significantly enhanced or reduced by overexpression of KIAA1429 or ALKBH5, respectively. (J) MeRIP assay showed that overexpressing KIAA1429 or silencing ALKBH5 notably increased the quantity of pri-miR-143-3p modified by m6A. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM (N ≥ 3 per group); *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001.