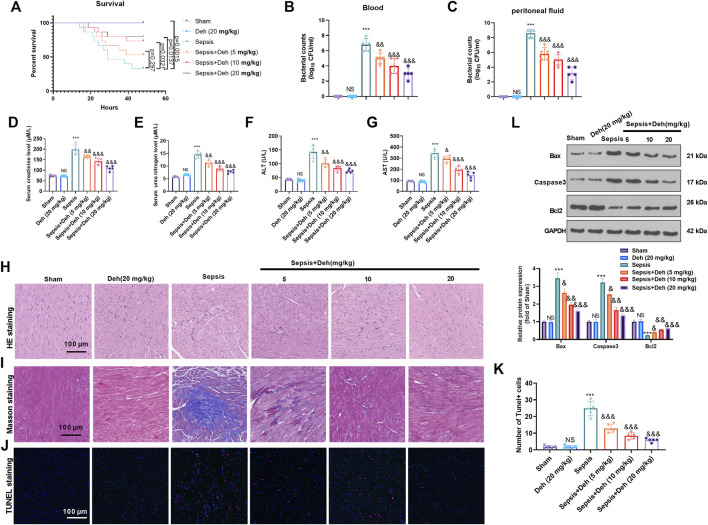
FIGURE 1.
Deh attenuated sepsis-mediated myocardial damage. The in-vivo model of sepsis in C57BL/6 mice was induced by intraperitoneal injection of Escherichia coli (E. coli). Deh (5–20 mg/kg body weight) was administered into the mice via intraperitoneal injection. (A) The survival (within 48 h after modeling) of mice was analyzed via the Kaplan Meier method. (B, C) The bacterial counts in the collected peritoneal lavage fluid and serum were calculated. (D–G). The levels of creatinine, urea nitrogen, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) in the supernatant of peritoneal lavage fluid and serum were measured using an automatic biochemical analyzer. (H, I) HE staining and Masson staining were used to detect myocardial injury in different groups of mice. (J, K) TUNEL-labeled apoptosis cells were detected using the TUNEL-detection kit. The number of TUNEL-positive cell were counted. (L) Western blot was carried out to examine the protein levels of Bax, Caspase3 and Bcl2 in the myocardial tissues. NS p > 0.05, ***p < 0.001 (vs. Sham group); & p < 0.05, && p < 0.01, &&&p < 0.001 (vs. Sepsis group). N = 5.