Figure 1.
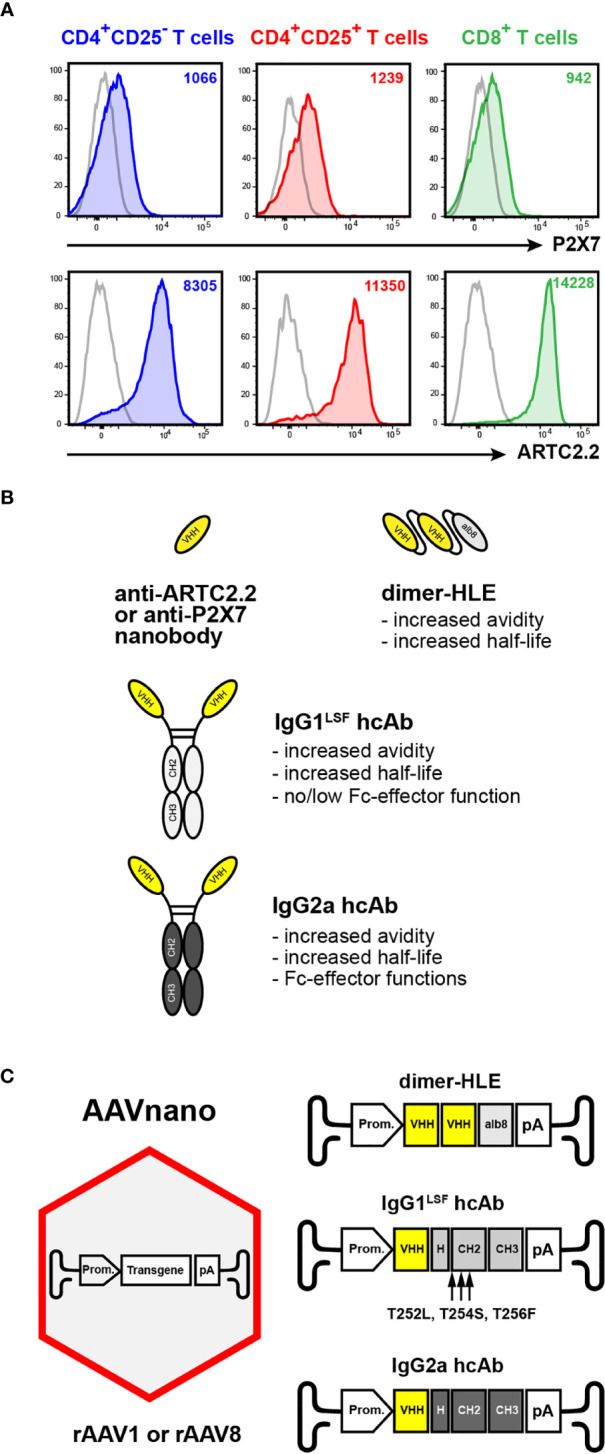
AAVnano methodological approach to study the role of P2X7 or ARTC2.2 in vivo. (A) Expression of ARTC2.2 and P2X7 T cell subsets. Splenocytes from C57BL/6 mice were stained with fluorochrome-conjugated monoclonal antibodies directed against P2X7 (clone 1F11), or ARTC2.2 (clone Nika102), or with the corresponding isotype controls (grey), and were analyzed by flow cytometry. Cells were gated on CD4+CD25- T cells (Tconv, depicted in blue), on CD4+CD25+ (Treg, depicted in red), or on CD8+ T cells (depicted in green) to evaluate the cell surface levels of P2X7 or ARTC2.2 on each subset. The numbers in the upper right quadrants indicate the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI). Staining was performed using fluorochrome conjugated antibodies specific to CD45 (coupled to BV510), CD4 (BV786), CD8 (BV605), CD25 (PE-Cy7), P2X7 (BV421) and ARTC2.2 (AF647). (B) Schematic representation of nanobody-based constructs. ARTC2.2-specific and P2X7-specific nanobodies (VHH) are engineered either as bivalent dimers fused to the albumin-specific nanobody Alb8 (dimer half-life extended, termed “dimHLE”), or as heavy-chain antibodies (termed hcAb) when fused to the hinge and Fc-region of conventional mouse IgG antibodies. For the latter, nanobodies were fused to either a mouse IgG1 hinge/Fc-region bearing the LSF mutations (i.e., T252L, T254S, T256F) to produce hcAb with no/low Fc-effector functions, or to the hinge/Fc-region of mouse IgG2a to generate cell-depleting hcAb. (C) Schematic representation of the AAVnano methodological approach and the structure of the transgenes incorporated in the rAAV (of serotype 1 or 8). The illustrated transgenes encode the nanobody-based constructs depicted in (B) Upon a single i.m. injection of the rAAV, the nanobody-based biologics are produced in vivo by the transduced muscle cells under the control of a CBA (rAAV1) or a CASI (rAAV8) promoter (Prom.).
