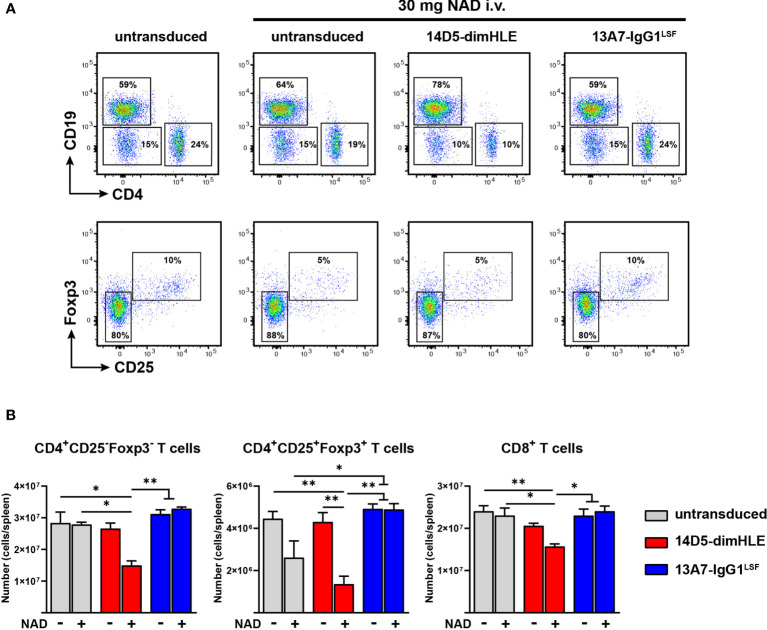
Figure 5.
AAVnano modulate in vivo the sensitivity to NAD+-induced cell death. C57BL/6 mice were injected i.m. with PBS (control) or with rAAV1 encoding the P2X7-potentiating 14D5-dimHLE construct or the P2X7-blocking 13A7-IgG1LSF hcAb construct. 28 days later mice were injected i.v. with PBS or 30 mg NAD+. Splenocytes were collected one day after and analyzed by flow cytometry to evaluate the levels of P2X7-dependent T cell depletion induced by NAD+ injection. (A) Representative flow cytometry plots showing the relative percentages of cells in each group. In the upper panels, CD4+, CD8+ and CD19+ lymphocytes were concatenated in the same subpopulation and analyzed together to visualize the level of depletion of CD4+ and CD8+ (CD4-/CD19-) T cells as compared to NAD+-insensitive CD19+ B cells. In the lower panels, the gated CD4+ cells were analyzed for both, expression of Foxp3 and CD25 to evaluate the percentages of Treg depletion in each group. Numbers indicate the percentage of cells in each indicated gate. (B) Absolute numbers of cells collected from spleen of untransduced control mice (grey) or from mice injected with rAAV encoding 14D5-dimHLE (red) or for 13A7-IgG1LSF hcAb (blue). Each group was injected i.v. either with PBS (-) or with 30 mg of NAD+ (+). Error bars represent the SEM. The statistical analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA (n=3 in each group, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). Staining was performed using fluorochrome conjugated antibodies specific to CD45 (coupled to BV510), CD4 (APC-Cy7), CD8 (BV605), CD19 (PerCP-Cy5.5), CD25 (PE) and FoxP3 (BV421).