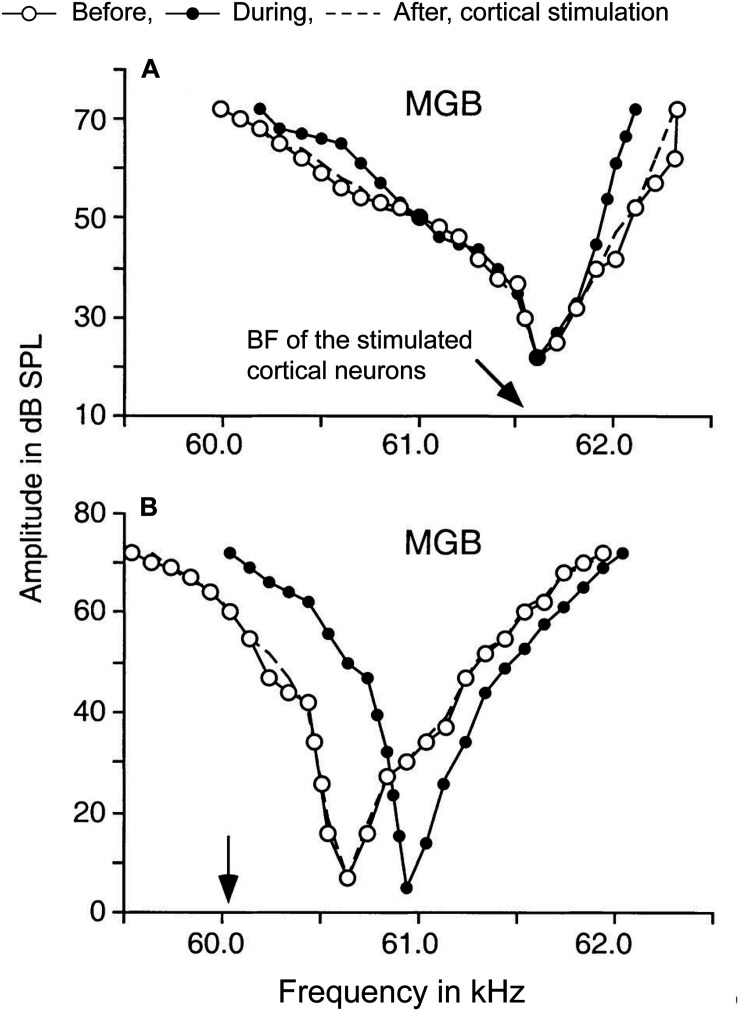
FIGURE 3.
Corticothalamic modulation of frequency tuning curves in MGBv neurons. A focal electrical activation of cortical neurons in the Doppler-shifted constant frequency processing area of Jamaican mustached bats evoked changes of frequency tuning curves in MGBv neurons. The black arrows indicate the best frequencies (BFs) of cortical neurons stimulated. The tuning curves were estimated before (white circles), during (black circles), and after (dashed lines) the cortical stimulation. (A) A MGBv neuron showed sharpening of the tuning curve when cortical neurons that had matched BF to the recipient MGBv neuron. BF of the MGBv neuron did not change. (B) Another MGBv neuron showed a reduction of responses around BF of the MGBv neuron when BF of stimulated cortical neurons is unmatched to the recipient MGBv neuron. The tuning curve was shifted away from the BF of stimulated cortical neurons with increasing responses outside of BF of the MGBv neuron. The changes were transient only lasting 1–2 h after the 7-min cortical stimulation (Adapted and modified with permission from Zhang and Suga, 2000; Figure 5).