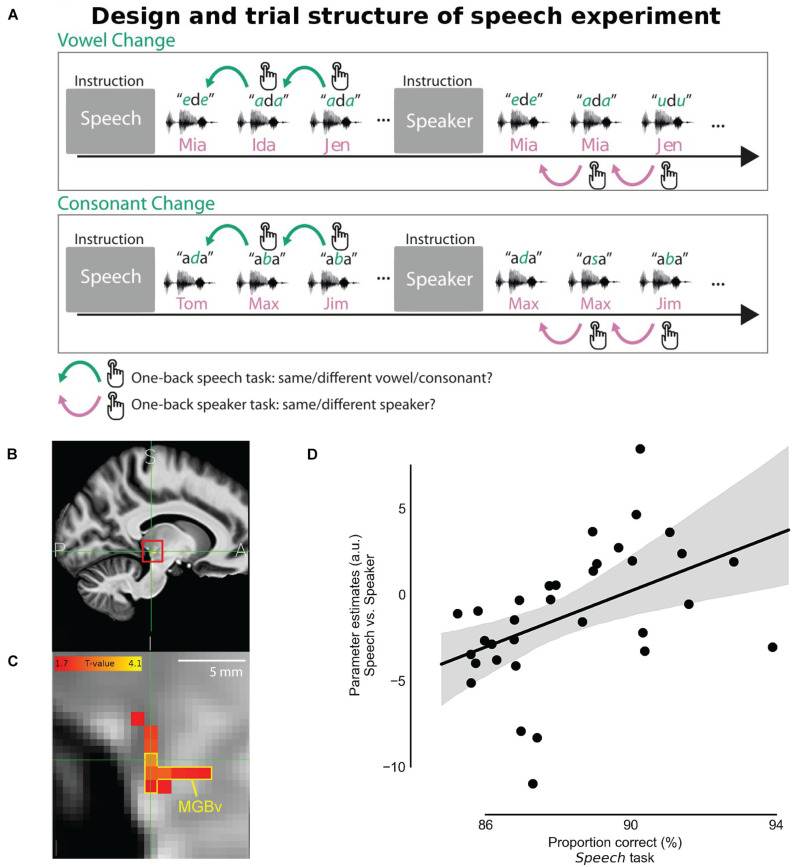
FIGURE 7.
Task-dependent modulation in MGBv for speech recognition. (A) Behavioral task design. In the speech task, participants pressed a button when a syllable changed in the sequence of vowel-consonant-vowel-syllables stimulus. In the speaker task, using exactly the same stimulus, they were instead asked to report when speaker identity changed in regardless of syllable changes. (B) The panel shows the averaged structural image by fMRI (sagittal section) across participants on the human brain atlas. The location of the left MGB was estimated and indicated with the red square. A, anterior; I, inferior; P, posterior; S, superior. (C) Zoomed view of the red square in the panel B, denoting MGBv by the yellow contour. The strength of the correlation between the speech vs. speaker task contrast and the averaged behavioral correct performance rate in the speech task was depicted with hot color coding. (D) Speech vs. Speaker tasks activation at the left MGBv coordinates correlated with the proportion of correct responses in the speech task. The better behavioral performance in the speech task corresponded to the larger difference of BOLD response between speech and speaker tasks in the left MGBv. Dots represent individual participants. The line shows the best fit with the gray area indicating 97% bootstrapped confidence interval (Adapted and modified with permission from Mihai et al., 2019; Figures 1C, 6, 7).