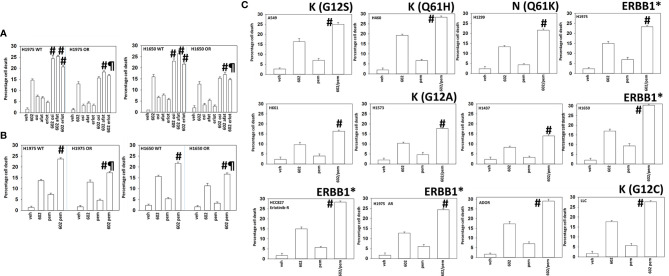
Figure 2.
GZ17-6.02 interacts with pemetrexed to kill NSCLC cells. (A) H1975 and H1650 cells [wild-type sensitive and osimertinib resistant (OR)] were treated with vehicle, erlotinib (500 nM), afatinib (500 nM), osimertinib (100 nM), GZ17-6.02 (2 μM curcumin final), or the drugs in combination for 24 h. Cell viability was determined by trypan blue exclusion (n = 3 ± SD). # p < 0.05 greater than GZ17-6.02 alone; ¶ p < 0.05 less than the corresponding values in drug-sensitive cells. (B) H1975 and H1650 cells [wild-type sensitive and osimertinib resistant (OR)] were treated with vehicle, pemetrexed (500 nM), GZ17-6.02 (2 μM curcumin final), or the drugs in combination for 24 h. Cell viability was determined by trypan blue exclusion (n = 3 ± SD). # p < 0.05 greater than GZ17-6.02 alone; ¶ p < 0.05 less than the corresponding values in drug-sensitive cells. (C) NSCLC cells were treated with vehicle, pemetrexed (500 nM), GZ17-6.02 (2 μM curcumin final), or the drugs in combination for 24 h. Cell viability was determined by trypan blue exclusion (n = 3 ± SD). # p < 0.05 greater than GZ17-6.02 alone. The mutational status of K-/N-RAS or of ERBB1 is noted in each graph. * = mutated active