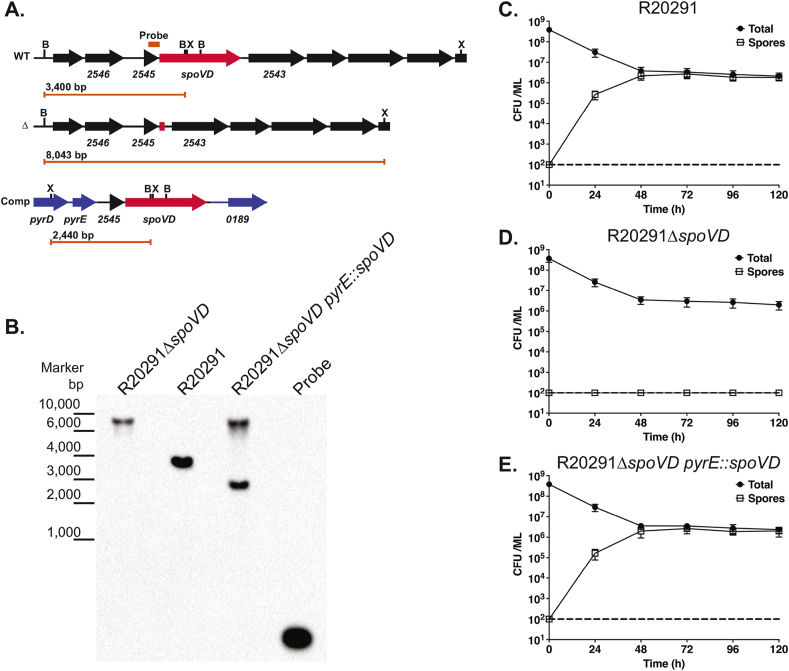
Fig. 1.
Sporulation requires SpoVDCd. A. Genomic organisation of the native spoVDCd locus (WT), following deletion of the spoVDCd gene (Δ) and following complementation by insertion of R20291_2545 and spoVDCd between the pyrE and R20291_0189 genes (Comp). The locations of XmnI (X) and BsrGI (B) sites are indicated, as is the annealing site of the Southern blot probe. The length of the diagnostic restriction product containing the probe sequence is also shown below each locus diagram. B. Southern blot analysis of a spoVDCd mutant (R20291ΔspoVD), the wild type parental strain (R20291) and complemented strain (R20291ΔspoVD pyrE:spoVD). A DNA ladder is shown on the left hand side. The predicted fragment sizes and annealing site of the probe are shown in panel A. C.-E. Sporulation efficiencies of the wild type (C.), spoVDCd mutant (D.) and complemented strains (E.). Stationary phase cultures were incubated anaerobically for 5 days with samples taken daily to enumerate total colony forming units (CFUs) and spores, following heat treatment to kill vegetative cells. Experiments were performed in duplicate on biological triplicates with mean and standard deviation shown. The dotted horizontal line indicates the limit of detection of the experiment.