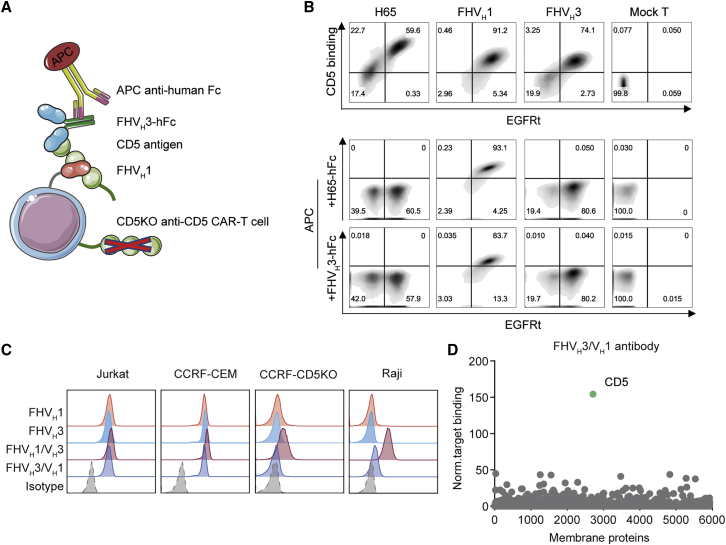
Figure 2.
CD5 antigen binding assay and competitive binding analysis of VH and validation of anti-CD5 biepitopic antibodies
(A) Schematic diagram of the anti-CD5 VH binding using a competitive fluorescence-activated cell sorting assay. (B) Representative flow cytometry analysis shows that H65, fully human (FH)VH1, and FHVH3 CAR-T cells all bind to CD5 antigen. FHVH3 recognizes the overlapped epitope of CD5 as H65, whereas FHVH1 binds different CD5 antigen epitopes with FHVH3 and H65. (C) Binding specificities of anti-CD5 biepitopic antibodies are shown. CD5+ cell lines (Jurkat and CCRF-CEM) and CD5− cell lines (CCRF-CD5KO and Raji) were stained with isotype control, FHVH1-hFc, FHVH3-hFc, FHVH1/VH3-hFc, and FHVH3/VH1-hFc antibody, respectively, followed by a secondary APC-labeled anti-human IgG, and analyzed using FACS. (D) Binding of FHVH3/VH1 to QT6 cells individually expressing 5,900 full-length human membrane proteins as determined by flow cytometry is shown.