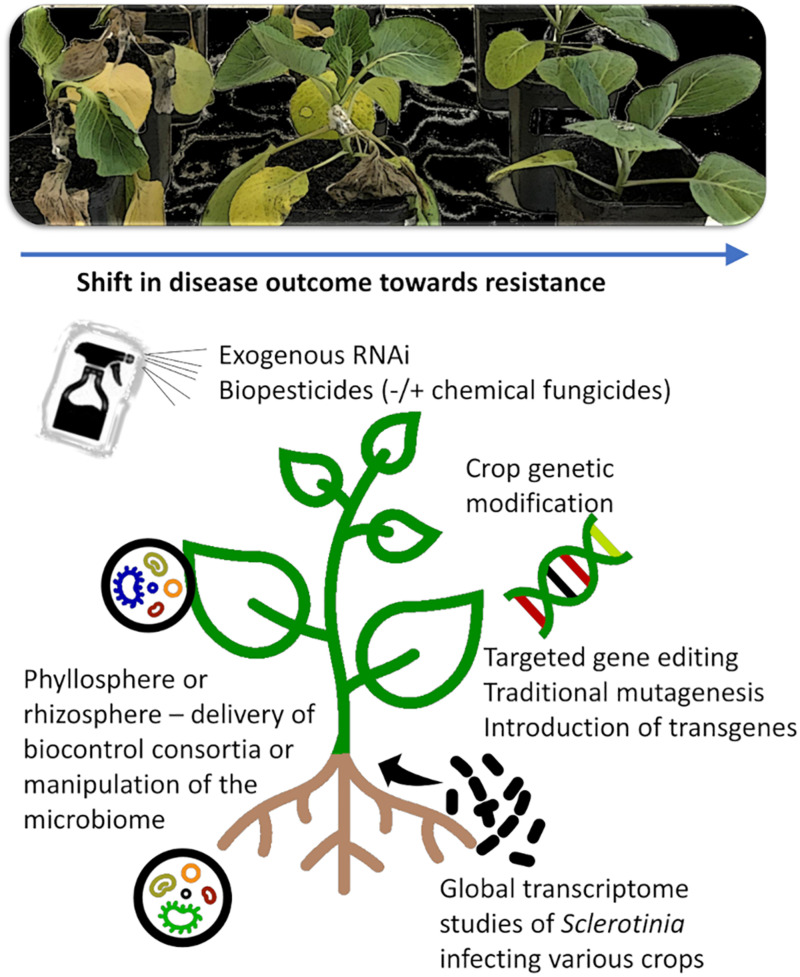
FIGURE 3.
New opportunities and tools for Sclerotinia control. New tools exist or are emerging that allow targeted manipulation of pathogen, host, or beneficial microbial populations that facilitate a reduction in Sclerotinia disease symptom development. These includes exogenous controls such as RNAi or biochemicals and biopesticides that can act directly on the pathogen (e.g., antifungal activity, fungal development) or indirectly by enhancing plant defense responses. Powerful endogenous controls such as crop genetic modification can provide durable resistance, but the process is costly, and not all crops are readily transformable or afford public acceptance. New knowledge of the pathogenicity and virulence of Sclerotinia species can be acquired through global omics studies on the pathogen infecting diverse crops of varying disease resistance, and this knowledge can be used to identify essential pathogen processes or weaknesses that can be targeted in new management tools.