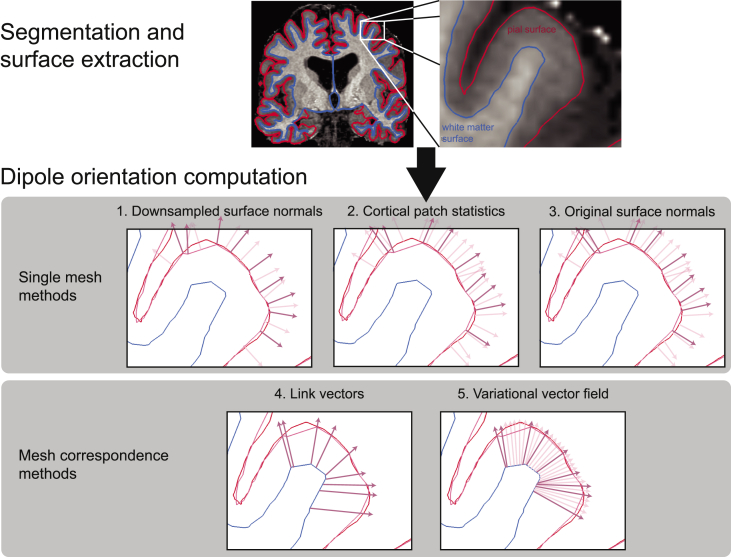
Fig. 1.
Dipole orientation models.
Pial and white matter surfaces are extracted from proton density and T1 weighted quantitative maps obtained from a multi-parameter mapping MRI protocol. Dipole orientation vectors are computed from these surfaces using five different methods. The downsampled surface normal and original surface normal methods compute vectors at each vertex (dark red) as the mean of the normal vectors of the surface faces they are connected to (light red). The cortical patch statistics method computes the mean of the normal vertices adjacent to the corresponding vertices in the original mesh. The link vectors method computes vectors which link corresponding vertices on the white matter and pial surfaces. The variational vector field method constructs a field of vectors which are approximately parallel to each other and orthogonal to the pial surface (shown in light red for the original surfaces and dark red for the subset of vertices in the downsampled surfaces).