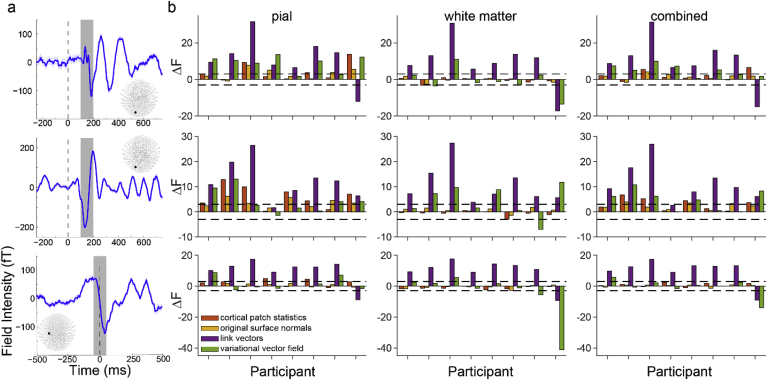
Fig. 6.
Surface correspondence-based methods yield the best model fit.
a Trial-averaged event-related fields (ERFs) aligned to the onset of visual stimulus 1 (the random dot kinematogram; top), visual stimulus 2 (the instruction cue; middle), and to the participant’s response (button press; bottom). Data shown are for a single representative participant. The inlays show the MEG sensor layout with filled circles denoting the sensor from which the ERFs are recorded. Each shaded region represents the time window over which source inversion was performed. b Change in free energy (relative to the downsampled surface normals model) for each method tested for each participant for visual ERF 1 (top), visual ERF 2 (middle), and the motor ERF (bottom) using vectors derived from 800 μm3 MPM volumes and source space models based on the pial (left), white matter (center), and combined pial/white matter surfaces (right).