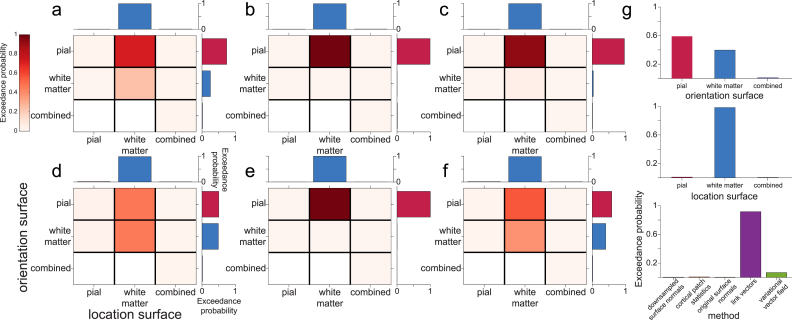
Fig. 7.
Source inversion using the pial surface and surface correspondence-based methods yield the best model fit overall.
a-e Exceedance probabilities for each combination of source space orientation (pial, white matter, and combined) and location (pial, white matter, and combined) models for each dipole orientation vector method tested (a downsampled surface normals, b cortical patch statistics, c original surface normals, d link vectors, e variational vector field) using surfaces derived from 800 μm3 MPM volumes. In each panel the top and right plots show exceedance probabilities for models grouped by source space location or orientation model alone. f As in a-e, for each source space orientation and location models over all dipole orientation vector methods. g Exceedance probabilities for each source space orientation model over all source space location models and dipole orientation vector methods (top), for each source space location model over all source space orientation models and dipole orientation vector methods (middle), and for each dipole orientation vector method over all source space orientation and location models (bottom).