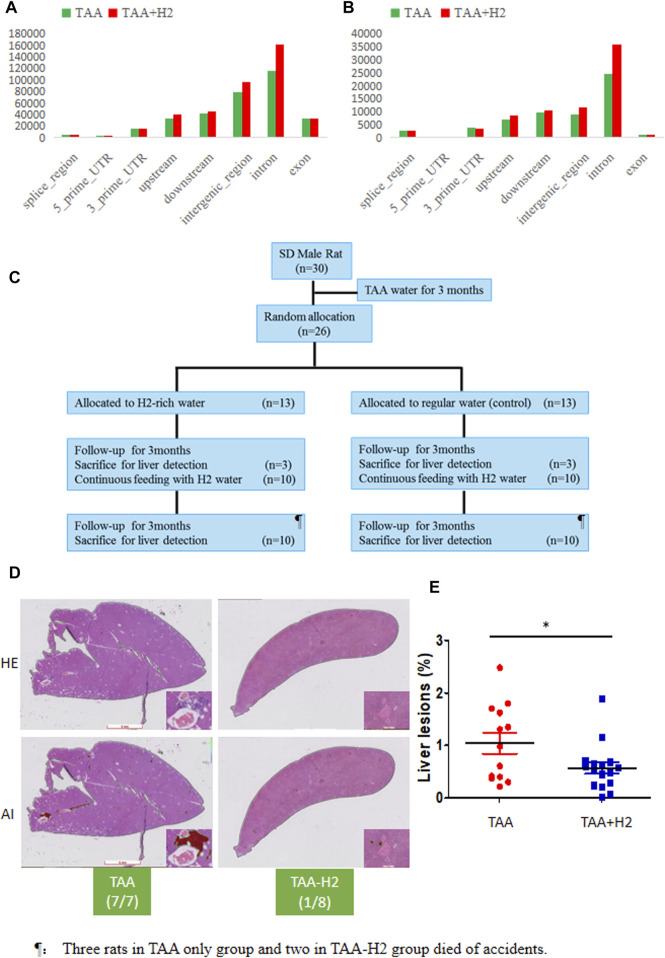
FIGURE 5.
Long-term use of H2-rich water interrupts the TAA-initiated cholangiofibrosis. (A, B) RNA-seq showed the number of SNP (A) and deletion/insertion (B) in the liver lesions from the TAA and TAA + H2 groups. (B) An experimental flow chart was designed to assess whether molecular hydrogen could interrupt the procession of cholangiofibrosis. (C) All rats developed cholangiofibrosis or suspicious cholangiofibrosis in TAA-pretreated rats without following treatment, while only one rat developed cholangiofibrosis if treated with H2-rich water. (D) The ratio of liver lesions determined by the AI algorithm in two groups. *p < 0.05.