Figure 1.
Subgenomic AAV vector molecules with increased risk for cancer formation by “readthrough” gene activation.
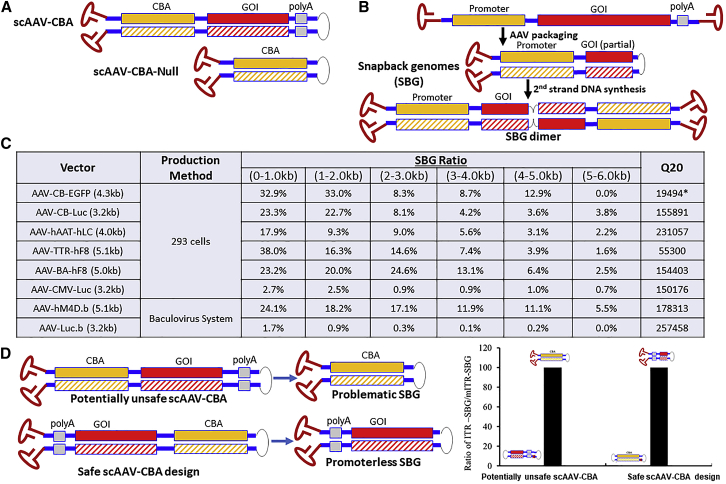
(A) Illustration of known vector designs that induce genotoxicity as described previously in Molecular Therapy (CBA, CMV enhancer/chicken beta actin promoter).1 (B) Illustration of SBG formed during rAAV production and of the dimer that is formed upon 2nd stranded DNA conversion. (C) Summary of the amount of SBG molecules in rAAV preparations. The SBG ratio indicates the number of molecules with SBG configuration divided by the number of all sequenced rAAV genomes in the same size range (based on Pacbio Single Molecules analysis of pooled vector DNA). For example, SBG in size range 4,000–5,000 means the complementary region is 2,000–2,500 nucleotides. Q20: long reads with = Q20 (99%) single-molecule accuracy generated using the circular consensus sequencing analysis method. SEQUEL sequencing was used, except for the one RSII sequencing library indicated with asterisks (∗), which had shorter reads. (D) Comparison of two scAAV vector designs. Placing the promoter in close proximity to the mutant ITR (which lacks the terminal resolution site) produces dimeric forms beneficial for transgene expression (with 2 copies of the enhancer in close proximity) and generates only “harmless” SBGs lacking a promoter. Vectors with either orientation were produced and sequenced. Problematic SBG contents was determined and graphed.