FIGURE 3.
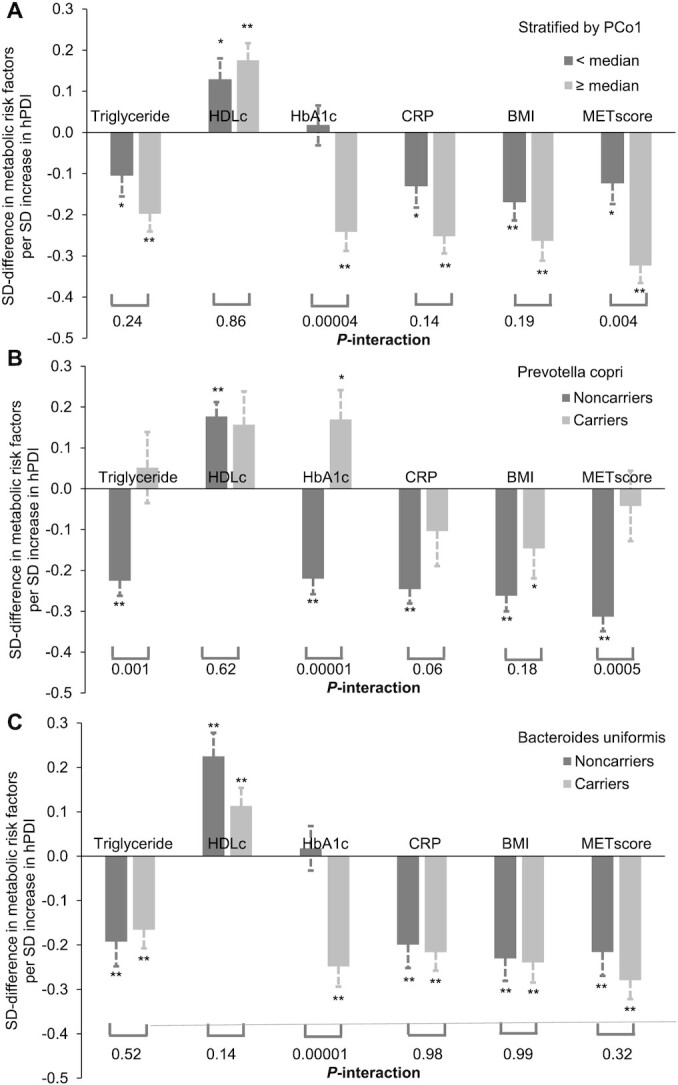
Interactions between microbiome and hPDI on metabolic risk factors based on 911 repeated measurements of the 303 participants. *0.01 < P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; associations between hPDI and metabolic risk factors were calculated from a linear mixed model that included participant's identifier as random effects and the hPDI, PCo1 score, or Prevotella copri/Bacteroides uniformis carriages, as well as simultaneously adjusting for age, energy intake, alcohol, smoking, physical activity, using of antibiotics, consumed any probiotics, and fecal sample characteristics. P-interactions between hPDI and the first PCo (A), the P. copri carriage (B), and B. uniformis (C) on individual and/or overall metabolic risk were calculated from the same models by further including the product term. Triglyceride, HDLc, HbA1,c and CRP were plasma concentrations. CRP, C-reactive protein; HbA1c, glycated hemoglobin; HDLc, HDL concentration; hPDI, healthy plant-based diet index; MET, metabolic risk; PCo; principal coordinate.
