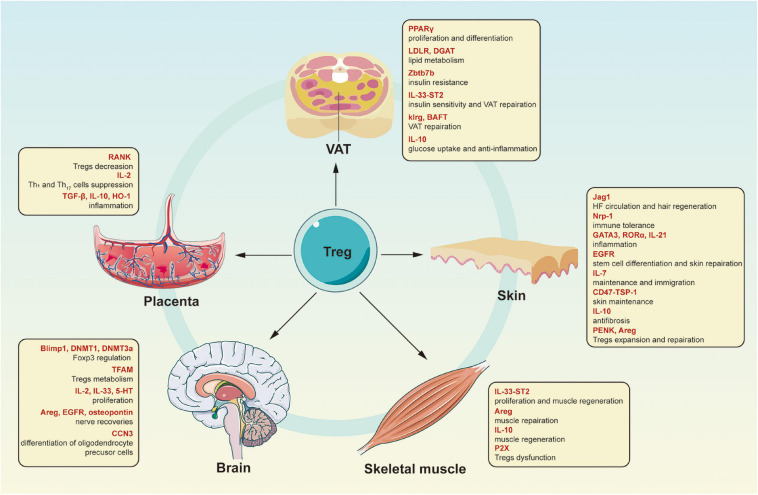
FIGURE 1.
Characteristics of different kinds of tissue Tregs. Tregs are not only critical for affecting immune response, but also for maintaining non-lymphoid tissues homeostasis via different cytokines or interacting with other tissue cells. Tregs, regulatory T cells; PPARγ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma; LDLR, low-density lipoprotein receptor; DGAT, diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase; Zbtb7b, Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 7B; IL-33, interleukin-33; ST2, IL-1 receptor-like 1; klrg1, killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily G1; BATF, basic leucine zipper ATF-like transcription factor; IL-10, interleukin-10; Jag1, the Notch signaling ligand Jagged1; Nrp1, neuropilin 1; GATA3, GATA binding protein 3; RORα, retinoic acid-related orphan receptor alpha; IL-21, interleukin-21; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; IL-7, interleukin-7; TSP-1, thrombospondin-1; PENK, proenkephalin; Areg, amphiregulin; P2X, purinergic receptor P2X; Blimp1, B lymphocyte-induced maturation protein 1; DNMT1, DNA methyltransferases 1; DNMT3a, DNA methyltransferases 3 alpha; TFAM, mitochondrial transcription factor A; IL-2, interleukin-2; 5-HT, 5-hydroxytryptamine; CCN3, cellular communication network factor 3; RANK, NF-κB ligand; TGF-β, transforming growth factor beta; HO-1, heme oxygenase 1.