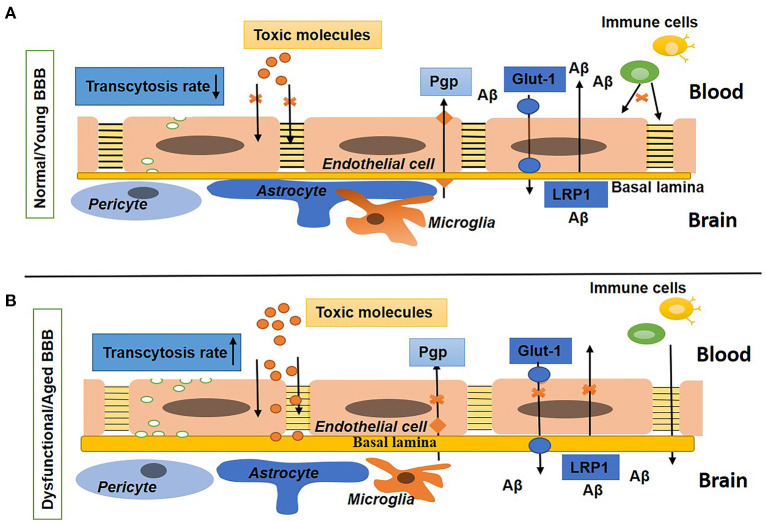
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram shows the normal/young blood–brain barrier (BBB) and dysfunctional/aged BBB. (A) Shows BBB in a young or normal state with tight and adherens junctions, a low rate of transcytosis, no diffusion of toxins, the presence of influx (Glut-1) and efflux (P-gp) transporters, and a low expression of leukocytes adhesion molecules (LAMs). The basal lamina is thin and surrounded by pericytes, astrocyte endfeet, and microglia. (B) Shows BBB in an aged or disease state with a high rate of transcytosis and diffusion of toxins, repression in influx and efflux transporters, upregulated expression of LAMs, and increased density of the extracellular matrix (ECM). Pericytes, astrocytes, and microglia are not associated with the basal lamina.