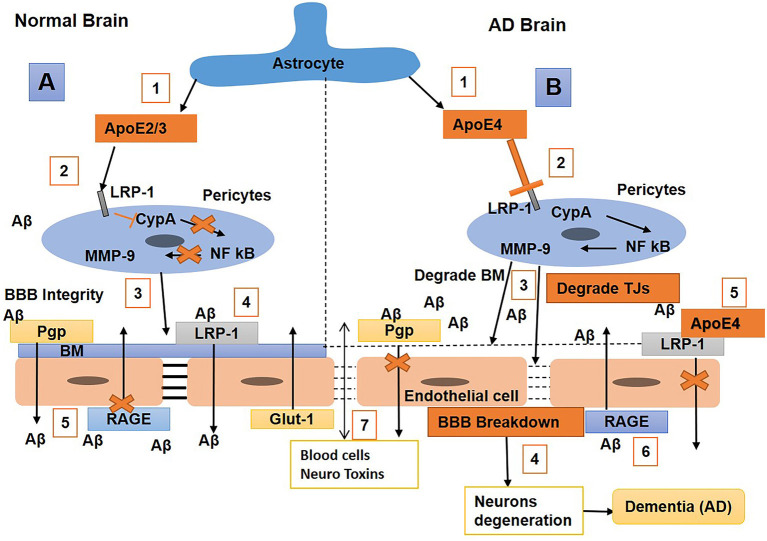
Figure 5.
Schematic diagram shows the mechanisms of blood–brain barrier (BBB) breakdown in a normal brain and one with Alzheimer's disease (AD). (A) Normal brain (1) Astrocytes release ApoE2/3, (2) bind with the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-1 (LRP-1) on pericytes and repress CypA-NFkB, which, in turn, stops matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9) secretion in pericytes; (3) hence, maintaining BM and BBB integrity, with (4) LRP-1 and P-gp on endothelial cells (ECs) also helping in amyloid-beta (Aβ) clearance. (5) Receptor for advanced glycosylation end products (RAGE) expression is repressed to stop the transport of Aβ into the brain. (B) AD brain (1) Astrocytes secret ApoE4, (2) weakly interact with LRP-1 on pericytes which activates the cyclophilin-A nuclear factor kβ matrix metalloproteinase 9 (CypA-NFkB-MMP9 pathways), (3) and result in BM and tight junctions (TJs) degradation leading to BBB breakdown, (4) associated with neurodegeneration and dementia. (5) ApoE4 also weakly interacts with LRP-1 on ECs that cannot significantly clear Aβ from the brain; hence, Aβ accumulates in the brain, causing neuronal damage. (6) Also, RAGE expression is upregulated, which promotes the transport of Aβ from blood to brain. (7) Blood cells and neurotoxins diffuse into the brain and cause neuronal loss and dementia.