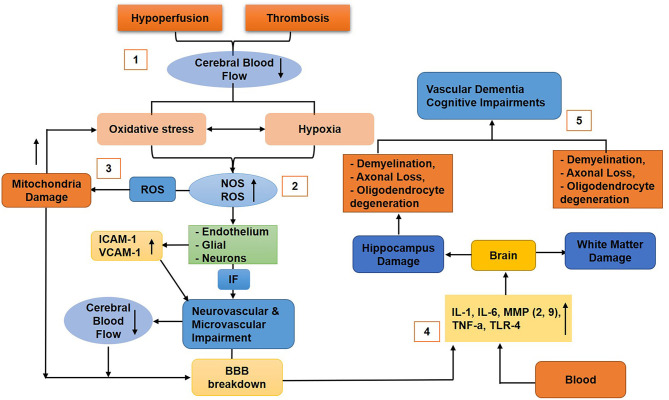
Figure 6.
Diagram that shows the molecular mechanism of blood–brain barrier (BBB) breakdown in vascular dementia. (1) Hypoperfusion and thrombosis cause reduced cerebral blood flow (CBF), thus generating oxidative stress and hypoxia (2), which upregulate nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species (ROS) that stimulate the endothelial (ICAM-1, VCAM-1 upregulated), glial, and neuronal cells to release inflammatory factors that cause neurovascular unit (NVU) impairment and reduce CBF and BBB disruption. (3) ROS damage mitochondria of the BBB cells that will further upregulate oxidative stress, resulting in BBB impairments. (4) Cytokines, chemokines, toxins, and other inflammatory molecules infiltrate the brain and cause damage to the hippocampus and white matter (5) associated with neuronal loss, vascular dementia, and cognitive impairments.