Figure 1.
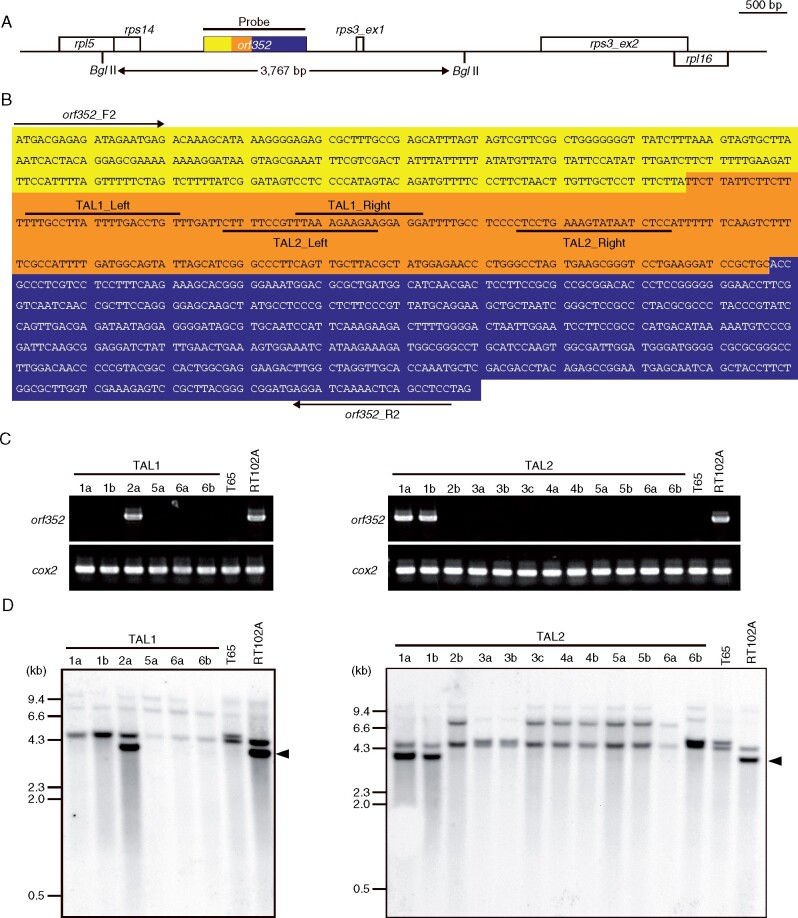
Introduction of the mitoTALENs TAL1 and TAL2, targeting orf352, into the RT102-type CMS rice (RT102A). A, Schematic illustration of the target gene orf352 and the neighboring region in the RT102-type mitochondrial genome. Yellow, region identical to orf284; navy blue, region homologous to orf288; orf352-specific sequences are shown in orange. rpl5, ribosomal protein L5; ψrps14, pseudo ribosomal protein S14; rps3_ex1, exon 1 of ribosomal protein S3; rps3_ex2, exon 2 of rps3; ψrpl16, pseudo ribosomal protein L16. B, Nucleotide sequences of the orf352 coding region. Background colors are as in (A). Primers for PCR analysis (orf352_F2, orf352_R2) are shown, as well as each TAL binding site. C, Genotyping of transgenic plants by PCR over the orf352 region. T65 is a fertile japonica rice cultivar that lacks orf352 and served as a negative control. Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 2 (cox2) is a positive control for amplification. The same images of orf352 are used in Supplemental Figure S3. D, Southern blot analysis of transgenic plants with TAL1 and TAL2-specific probes. Arrowheads indicate signals corresponding to a 3.8-kb orf352 fragment. The data in (C and D) are representative of three independent experiments.