FIGURE 3.
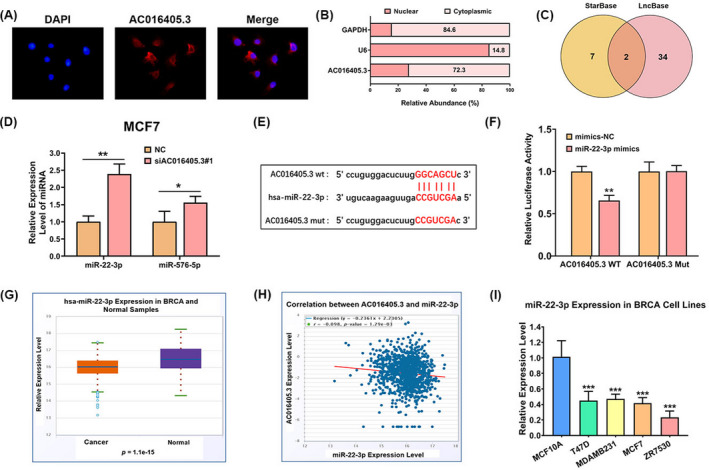
AC016405.3 is mainly distributed in the cytoplasm and directly targets miR‐22‐3p. (A) FISH indicated the subcellular location of AC016405.3 in MCF7 cells (red). (B) Relative expression levels of AC016405.3 in nuclear and cytosolic fractions of MCF7 cells. GAPDH and U6 were served as cytosolic and nuclear controls, respectively. (C) Target miRNAs of AC016405.3 obtained by intersecting the miRNAs predicted by starBase and LncBase. (D) The expression levels of miR‐22‐3p and miR‐576‐5p in MCF7 cells with or without the transfection of si‐AC016405.3. (E) The putative binding sites between AC016405.3 and miR‐22‐3p. (F) The direct interaction between AC016405.3 and miR‐22‐3p verified by dual‐luciferase assay. (G) Differential analysis of miR‐22‐3p and (H) correlation analysis between AC016405.3 and miR‐22‐3p based on starBase database. (I) Basic levels of miR‐22‐3p in normal breast epithelial cell line (MCF10A) and different BRCA cell lines, as detected with RT‐qPCR. Note: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.005
