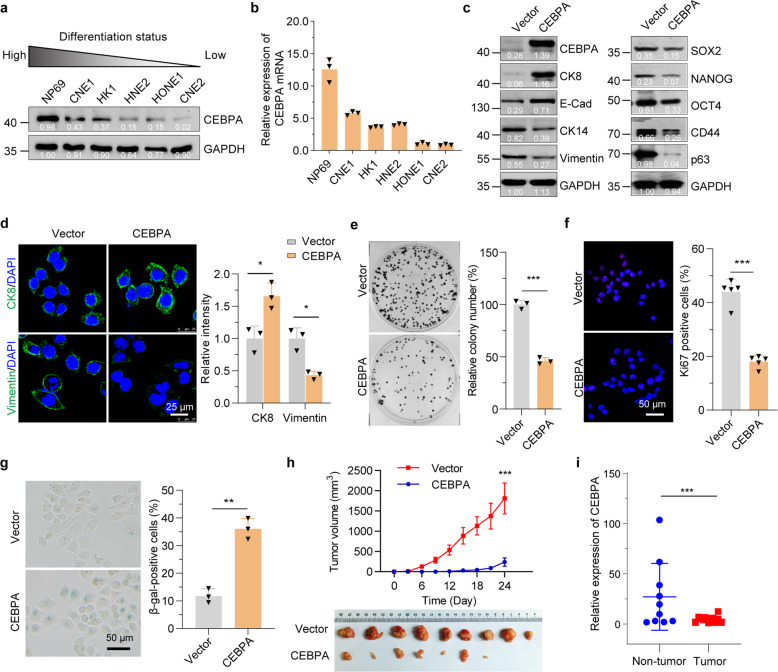
Fig. 3.
CEBPA drives cellular differentiation of NPC-derived cells. a Protein levels of CEBPA in various NPC-derived cell lines with different differentiation status. b RT-qPCR analysis of relative CEBPA mRNA levels in various NPC-derived cell lines with different differentiation status. c Western blot with differentiation and stem-like markers in control (Vector) and CEBPA-overexpressed (CEBPA) CNE2 cells. d Immunofluorescence analysis with differentiation markers in control and CEBPA-overexpressed CNE2 cells. e Colony formation in control and CEBPA-overexpressed CNE2 cells. f Immunofluorescence staining for Ki67 in control and CEBPA-overexpressed CNE2 cells. g SA-β-gal staining in control and CEBPA-overexpressed CNE2 cells. h CEBPA-overexpressed and control CNE2 cells were injected into nude mice subcutaneously, and tumor volume was determined. i RT-qPCR analysis of relative CEBPA mRNA levels in patients’ tumor tissues non-tumor nasopharyngeal tissues. Statistics (d–i), significance: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001; two-tailed Student’s t-tests