Figure 1: Generation of human neurons from induced pluripotent stem cells.
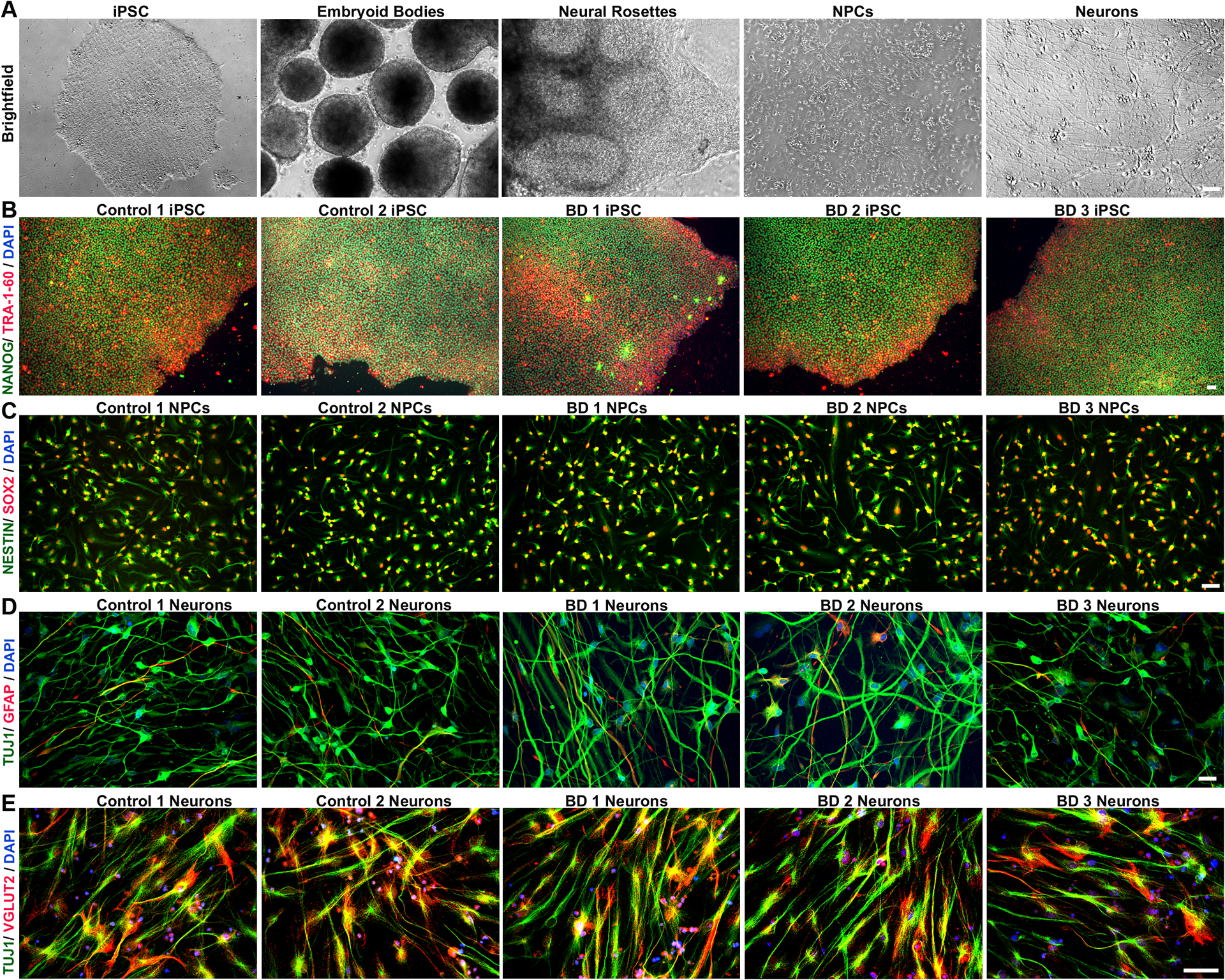
Control and BD iPSCs are morphologically similar, characterized by well-defined borders, circular shape and expression of pluripotency markers. (A) Brightfield images showing stages of embryoid bodies based neural differentiation paradigm for iPSCs. (B) Representative image of an iPSC clone co-labeled with pluripotency markers, TRA 1–60 (red), and NANOG (green). (C) NPCs generated from control and BD iPSCs co-express early cortical neural precursor markers NESTIN (green) and SOX-2 (red). (D) Differentiated neurons expressing the neuron-specific marker TUJ1, and only weakly express the glia-specific marker GFAP. (E) Representative images of control and BD neurons showing widespread co-localization of vesicular-glutamate transporter 2 (VGLUT2) in TUJ1 positive cells, indicating enrichment of glutamatergic neurons. Cell nuclei are stained with DAPI (B-E). Antibodies used are listed in Table S2. Scale bars = 50μm. BD: bipolar disorder; DAPI: 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; GFAP: glial fibrillary acidic protein; iPSCs: induced pluripotent stem cells; NPCs: neural progenitor cell; TUJ1: β-III tubulin; VGLUT2: vesicular-glutamate transporter Numbers in the titles were arbitrarily assigned for identification.
