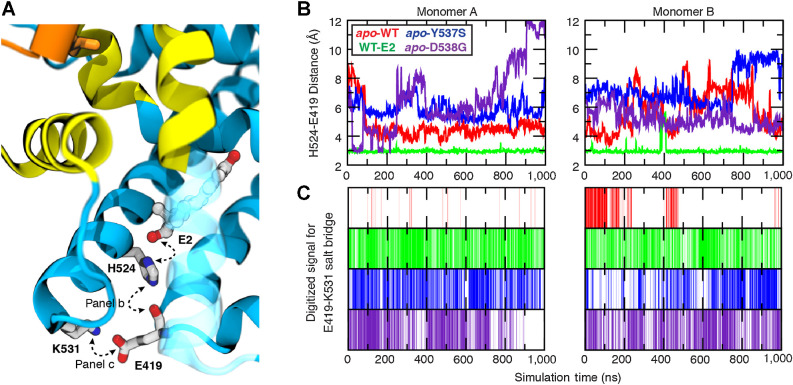
Figure 4.
Ligand-mediated hydrogen-bonding network correlates to receptor activity. The stability of key interactions forming a ligand-mediated hydrogen-bond network was quantified from microsecond simulations. A, The network is initiated by the 17β-hydroxyl group of E2 and proceeds through His524:Nε hydrogen bond to the carbonyl of Glu419, terminating with a salt bridge formed between Lys531 and Glu419. B, The His524–Glu419 interaction was monitored by measuring the distance between His524:Nε (donor) and Glu419 carbonyl oxygen (acceptor), whereas (C) the presence of the terminal salt bridge between Glu419 and Lys531 was monitored by digitizing the signal based on geometric constraints.