Table 1.
Summary table of the smart theranostics discussed in this section and their pH-responsive mechanisms
| Smart theranostic | Structure of responsive linker | Responsive trigger | Responsive Mechanism | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PMN/Ce6 |
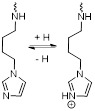
|
pH |
pH = 6.5-7: Ionisation of imidazole groups cause swelling. pH = 5.5: Further ionisation of imidazole groups causes disassembly and release of photosensitiser. |
113 |
| DOX@ES-MION3@RGD2@mPEG3 |
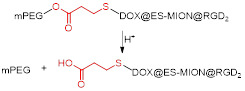
|
pH | pH = 5.5: Cleavage of β-propionate linker leads to exposure of RGD2 ligand and tumour cell internalisation. | 119 |
| Gd2O3@MSN-DOX |
|
pH | pH = 5.0: Charge reversal and disintegration of polyelectrolyte P(DMA-co-TPAMA) leads to DOX release. | 115 |
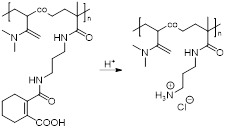
| MTX-Mn@PEG |
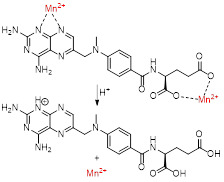
|
pH | pH = 5.5: Protonation of carboxylic acids and nitrogen heterocycle of MTX reduces coordination and releases Mn2+ from MTX complex. | 117 |
| SPA-SPIO-IR780 |


|
pH | pH = 6.5: Cleavage of bond between PEI and HHPA and exposure of positive amino groups enhances tumour cell internalisation. | 116 |
| Fe3O4@TA-PEG/ICG |
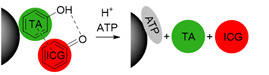
|
pH ATP |
pH = 5.5: Protonation of hydroxyl groups of TA leads to disassembly by weakening of coordinate and hydrogen bonds. Quenching of ICG is reduced. ATP (10 mM): Displacement of TA from the nanoparticles and disassembly. |
32 |
| Bi-MSx-PEG/DOX NFs |
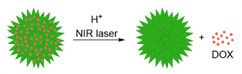
|
pH NIR light |
pH = 5.5: Solubility of DOX is increased. NIR laser: Temperature increase reduces binding of DOX to NPs, facilitating its release. |
118 |
| MCDION-Se |
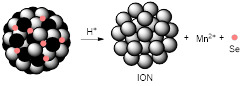
|
pH | pH = 5.5: Degradation of MnCO3 component of nanoparticles leads to release of Mn2+ and Se in tumour cells. | 128 |
| Gd-texaphyrin-DOX complex |
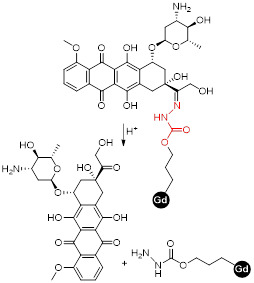
|
pH | pH = 5.5: Cleavage of hydrazone linker leads increase of FL signal of DOX due to separation from the Gd-texaphyrin complex. | 132 |
