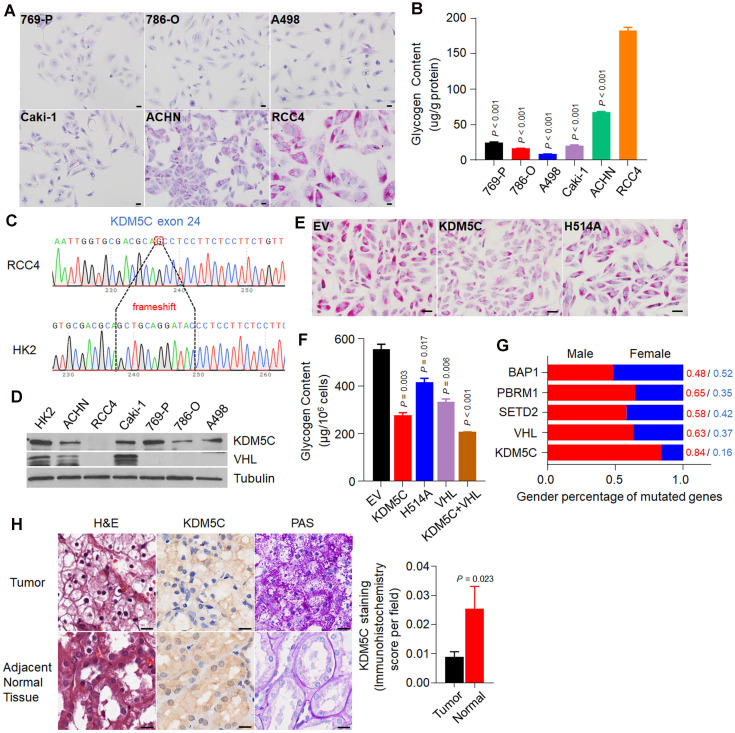
Figure 1.
X-inactivation escaping gene KDM5C harbors frame-shift mutation in ccRCC cell line with the highest glycogen level. A, Periodic acid-schiff (PAS) staining of a series of ccRCC cell lines. Scale bar, 20 µm. B, The glycogen level determination of indicated cell lines. C, The frame-shift mutation of KDM5C identified in RCC4 exome sequencing compared with HK2. D, The KDM5C and VHL protein level detected by Western Blot in various ccRCC cell lines. E, PAS staining of stable cell lines including RCC4-EV, RCC4-KDM5C, RCC4-H514A. Scale bar, 20 µm. F, Bar graph showing the intracellular glycogen content in indicated cells. G, Stacked bar graph showing the gender ratio of frequently mutated genes in KIRC. H, Representative hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stained (left), KDM5C immunohistochemically stained (middle), and PAS stained (right) sections from the tumor (top) and adjacent normal tissue (bottom). Scale bar, 40 µm. Bar graph showing the statistical analysis of indicated tissues stained with KDM5C antibody. P values were calculated using two-tailed Student's t-test. Data represent means ± SD. Data are representative of three independent experiments.