Figure 12.
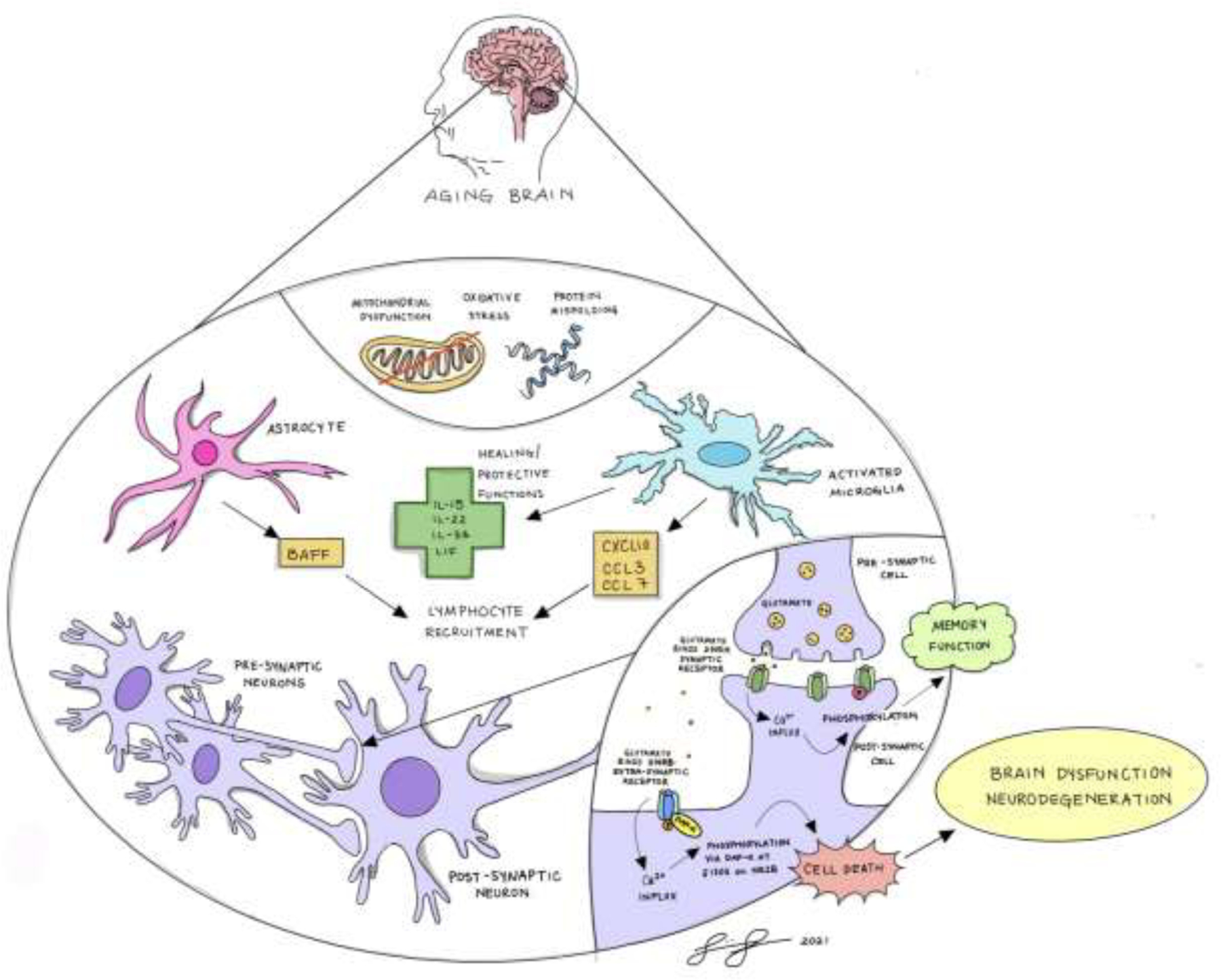
Summary schematic illustrates hypothetical model in which oxidative stress and metabolic demand from neurons in the LC and hippocampus accompany an increase in inflammatory signaling from astrocytes and microglia. Excessive glutamate release in aging brain leads to activation of extrasynaptic NMDA receptors predominantly containing NR2B subunits leading to impairment of neuronal function and behavioral impairment.
