FIGURE 2.
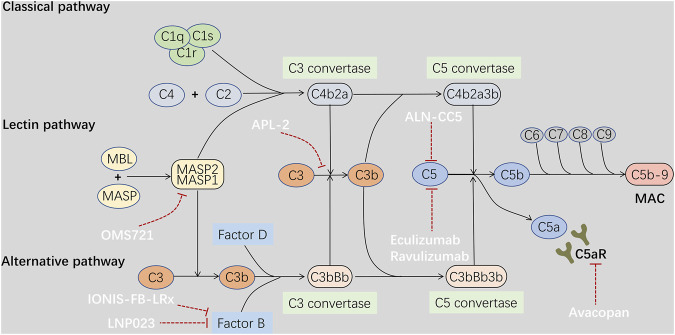
Drugs treat IgAN through regulation of complement activation. Complement activation through any of the three pathways ends up in activation of the terminal pathway, followed by cleavage of C5 by a C5 convertase, thereby leading to the release of C5a and formation of a membrane attack complex C5b-9. Circulating and mesangial polymeric IgA1 may activate both the alternative and lectin pathway systemically or locally in the glomeruli, resulting in deposition of complement fragments and glomerular inflammation in IgAN. C5a is an anaphylatoxin, which can induce an exaggerated inflammatory response through interaction with C5aR. In addition, C5b-9 deposition may stimulate inflammatory cytokines production by mesangial cells. Therefore, drugs targeting the alternative pathway Factor B and C3 such as LNP023, IONIS-FB-LRx, APL2, and the lectin pathway MASP2 such as OMS721, and the terminal pathway C5 and C5aR such as ALN-CC5, Eculizumab, Ravulizumab, Avacopan may be beneficial to IgAN through suppression of complement-dependent inflammation.