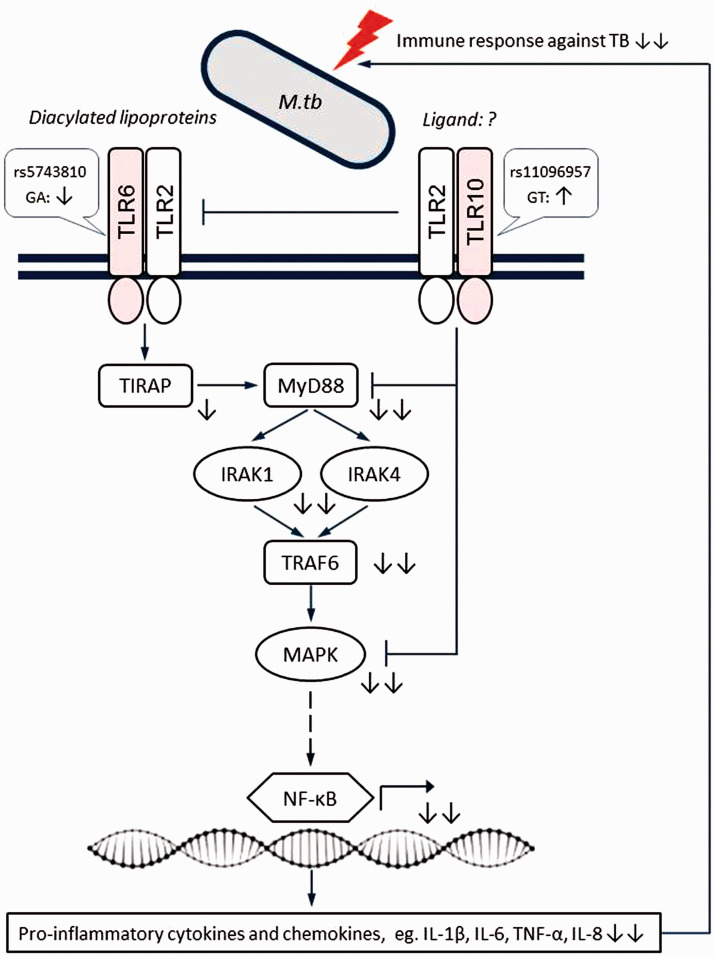
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the proposed epistatic/synergistic interaction between SNPs TLR6 rs5743810 and TLR10 rs11096957 in conferring susceptibility to TB based on the present results.TLR6 and TLR10 have largely opposite effects on the immune response, with TLR10 mainly having a suppressive function. Simultaneous suppression of TLR6 signaling and activation of TLR10 signaling caused by genetic variations may result in decreased pro-inflammatory responses against M. tuberculosis, thus increasing the risk of TB. Symbols indicate the following: sharp arrow – positive interaction; blunt arrow – negative interaction; solid line – direct interaction; dashed line – indirect interaction; question mark – unknown ligand partner; up/down arrows – activation/suppression; double arrows – synergistic effects of two mutations. Figure adapted from Oosting et al. (2014).10