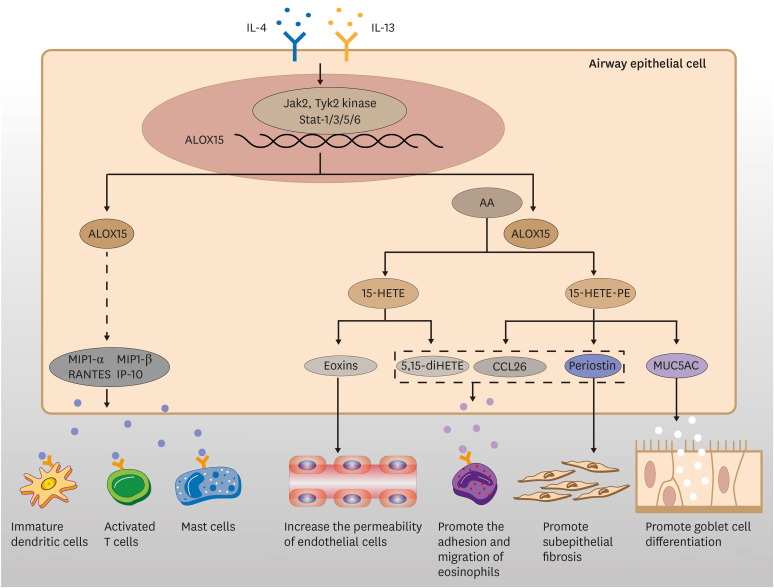
Fig. 1. Specific molecular metabolic pathways of ALOX15 and its reaction products in airway inflammation. ALOX15 induces the expression of chemokines such as MIP-1α, MIP-1β, RANTES, and IP-10, thus promoting the migration of immature dendritic cells, activated T cells, and mast cells. ALOX15 expressed in human airway epithelial cells catalyzes the conversion of AA into 15-HETE, which is then conjugated with PE to form 15-HETE-PE or further metabolized into biologically active molecules such as eoxins and 5,15-diHETE. 15-HETE-PE induces the expression of CCL26, MUC5AC, and periostin to promote the migration of eosinophils, the differentiation of goblet cells, the adhesion and migration of eosinophils, and subepithelial fibrosis, whereas eoxins increase the permeability of endothelial cells, and 5,15-diHETE promotes eosinophil infiltration.
ALOX15, arachidonic acid 15-lipoxygenase; MIP, macrophage inflammatory protein; RANTES, Regulated upon Activation, Normal T Cell Expressed and Presumably Secreted; IP-10, interferon-γ-inducible protein 10; AA, arachidonic acid; 15-HETE, 15-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; 5,15-diHETE, 5S,15S-dihydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid; CCL26, chemokine ligand 26; MUC5AC, mucin 5AC.