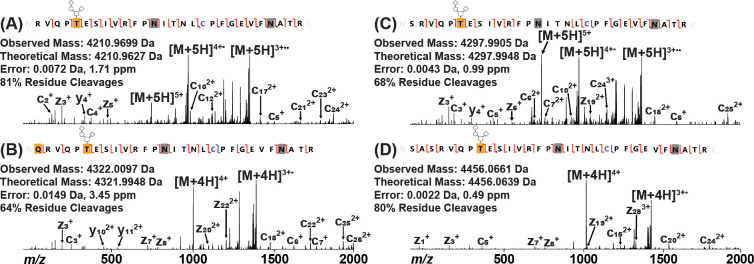
Figure 2.
Determining the N-terminus of RBD Protein by EThcD. (A) Predicted N-terminal peptide as found in M68, M69, and original Ragon Institute constructs. (B) N-terminal peptide found in M67 and original Mt. Sinai constructs containing an additional Gln residue. This Gln residue was modified to a pyroGlu residue, as noted by the yellow box. (C) N-terminal peptide found in M68, M69, and original Ragon Institute constructs containing an additional Ser residue. (D) N-terminal peptide found in M68, M69, and original Ragon Institute constructs containing additional Ser-Ala-Ser residues. Carbamidomethylated Cys is noted in blue, and deamidated Asn residues are noted by gray boxes. Observed c/z ions are noted by red flags between residues, while observed b/y ions are noted by blue flags. All peptides were found to be O-glycosylated with Hex(1)HexNAc(1)NeuAc(2) on the first Thr residue (T5 of RBD; T323 of full-length spike) as noted by the yellow box with glycan pictogram. The complementary ion pairs resulting from the backbone cleavage of T5/E6 and E6/S7 confirm the glycosylation localization.