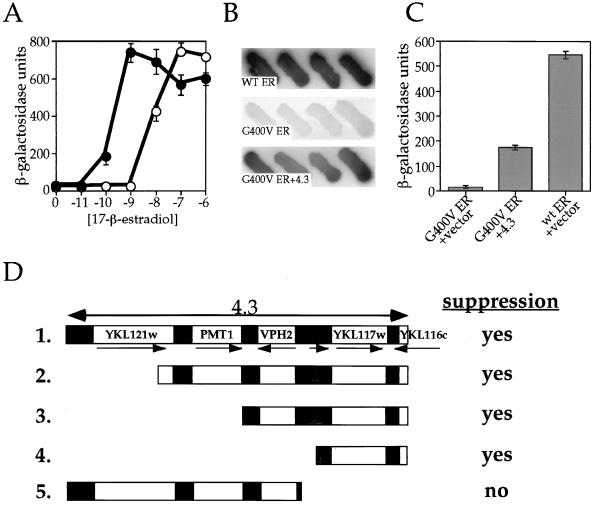
FIG. 1.
Isolation of a yeast genomic fragment that suppresses the G400V ER phenotype. (A) Transcriptional activity of wt ER and G400V ER as a function of 17-β-estradiol concentration. The W303a yeast strain was transformed with a galactose-inducible expression vector containing either wt or G400V ER, along with an ERE-containing β-galactosidase reporter plasmid. Transcriptional activation by wt ER (solid circles) and G400V ER (open circles) in response to increasing 17-β-estradiol concentration was determined by liquid β-galactosidase assay as described in Materials and Methods. Note that G400V ER requires a 100-fold-higher estradiol concentration to induce transcriptional activation than wt ER. The dosage suppression screen was carried out in the presence of 1 nM 17-β-estradiol, the conditions under which the G400V ER phenotype is most pronounced. (B) The relative activity of wt ER, G400V ER, and G400V ER plus suppressor 4.3. Four independent colonies on X-Gal indicator plates containing 1 nM 17-β-estradiol are shown and represent wt ER plus empty library plasmid (wt ER), G400V ER plus empty library plasmid (G400V ER), or G400V ER plus suppressor plasmid 4.3 (G400V ER+4.3). (C) Transcriptional activity of wt ER, G400V ER, and G400V ER in the presence of suppressor 4.3. Liquid β-galactosidase assays were performed on yeast strains containing wt ER plus empty library plasmid, G400V ER plus empty library plasmid, or G400V ER plus 4.3 at 1 nM 17-β-estradiol. Suppressor 4.3 increases G400V ER activity 10-fold, bringing its activity to nearly one-third that of wt ER. (D) Identification of YKL117w as the G400V ER suppressor. The sequence of the yeast genomic fragment contained within the suppressor 4.3 was determined by aligning the 5′ and 3′ ends of the insert to the yeast genomic sequence database. Suppressor 4.3 contains an 8,147-bp fragment comprising four complete ORFs (YKL121w, PMT1, VPH2, and YKL117w), a partial ORF (YKL116w), and a tRNA-Ala gene (shaded box). The relative positions and orientations of the genes within the 4.3 fragment are shown schematically (fragment 1). Identification of the gene responsible for suppressing the G400V ER phenotype was accomplished by constructing 5′ and 3′ deletion derivatives of the 4.3 suppressor (fragments 2 to 5) and assaying their ability to increase G400V ER transcriptional activity at 1 nM 17 β-estradiol. “yes” indicates that the fragment was capable of suppressing the G400V ER phenotype; “no” indicates that the fragment failed to increase G400V ER transcriptional activity. YKL117w was present within the suppressing fragments (fragments 1 to 4) but was absent within the fragment that did not suppress (fragment 5), suggesting that its gene product is responsible for increasing G400V ER transcriptional activation. YKL117w encodes the yeast homologue of the human p23 protein (yhp23).