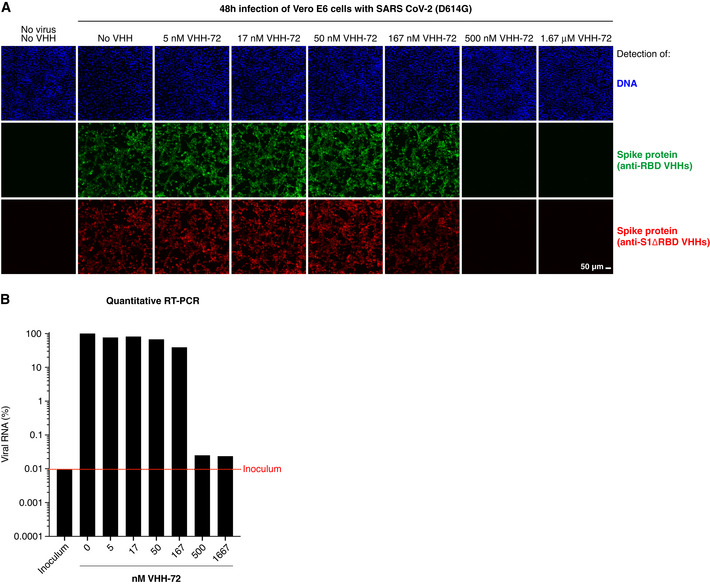
Vero E6 cells were infected with SARS‐CoV‐2, pre‐incubated with indicated concentrations of the neutralizing VHH‐72 (Wrapp
et al,
2020a). Cells were fixed two days after inoculation, stained with sets of anti‐RBD (green) and anti‐S1ΔRBD (red) nanobodies (see Fig
1B and C), and analyzed by CLSM. We used a cocktail of such fluorophore‐labeled VHH antibodies to ensure that negative fluorescence readings truly indicated neutralization and thus absence of viral infection and not just masking of the IF epitope by the tested nanobody. See Appendix Fig
S1 for independent biological replicates.