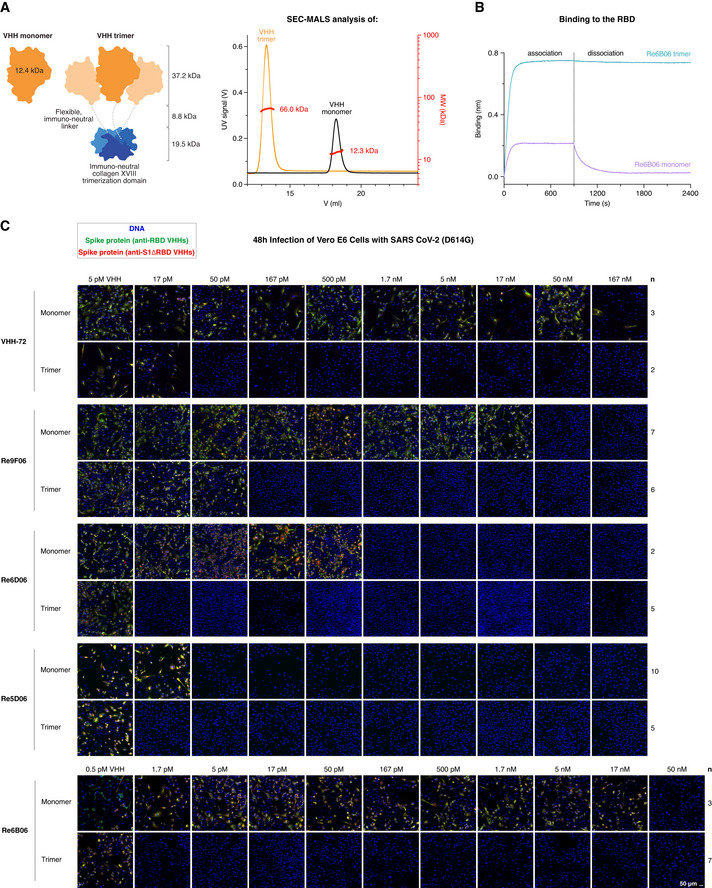
Left: Schematic representation of VHH antibodies produced in
E. coli as monomers or homo‐trimeric fusions with the human collagen XVIII trimerization module. The VHH trimers match the threefold rotational symmetry of the SARS‐CoV‐2 Spike protein. The molecular weight of the indicated modules is shown. Right: As an example, monomeric and trimeric forms of Re7H02 (a Re6B06 class member, Fig
1A) were analyzed by size exclusion chromatography (SEC, Superdex 200 column) coupled with multi‐angle light scattering (MALS). The elution profiles (UV absorbance signal), as well as the calculated molecular weights (per slice), are plotted, and the average molecular weight is indicated.