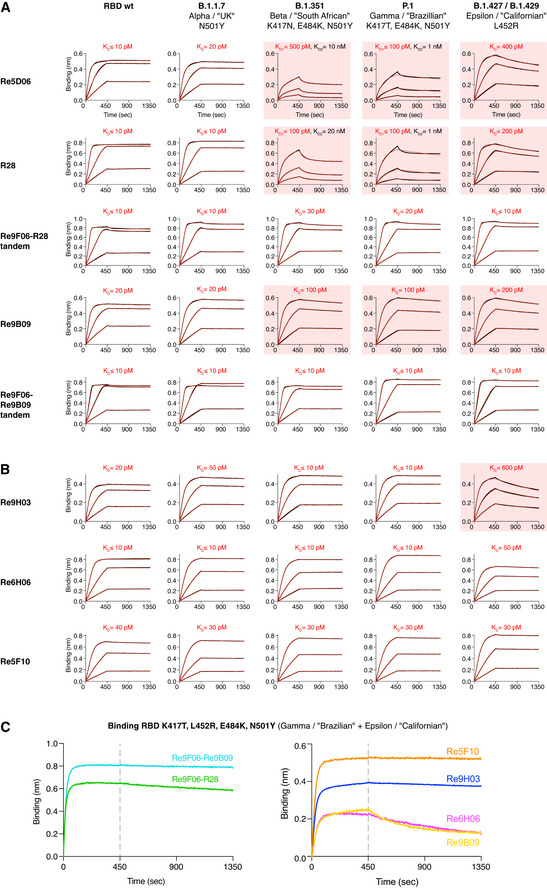
Figure 9. Characterization of VHH antibodies that tolerate major RBD escape mutations.
-
A, BThe indicated nanobody constructs were immobilized on BLI sensors and dipped into solutions containing 3‐fold dilutions of WT or mutant RBDs (20, 6.66, and 2.22 nM) for 450 s. RBD dissociation in assay buffer was followed for 900 s. The response curves with biphasic dissociations were fitted using a 2:1 model. All other curves were fitted using a mass transport model. RBDs with impaired VHH binding are highlighted with red boxes.
-
CBinding of nanobodies to the quadruple RBD mutant was monitored by BLI. Immobilized RBD was incubated with 100 nM of nanobodies for 450 s, followed by assay buffer for 900 s.
Data information: We use the simplified SARS‐CoV‐2 nomenclature proposed by the World Health Organization (WHO), but also provide the PANGO lineage identifier and the obsolete naming of variants by their geographic origin, because all of these naming conventions have been used in the literature cited in this work.
