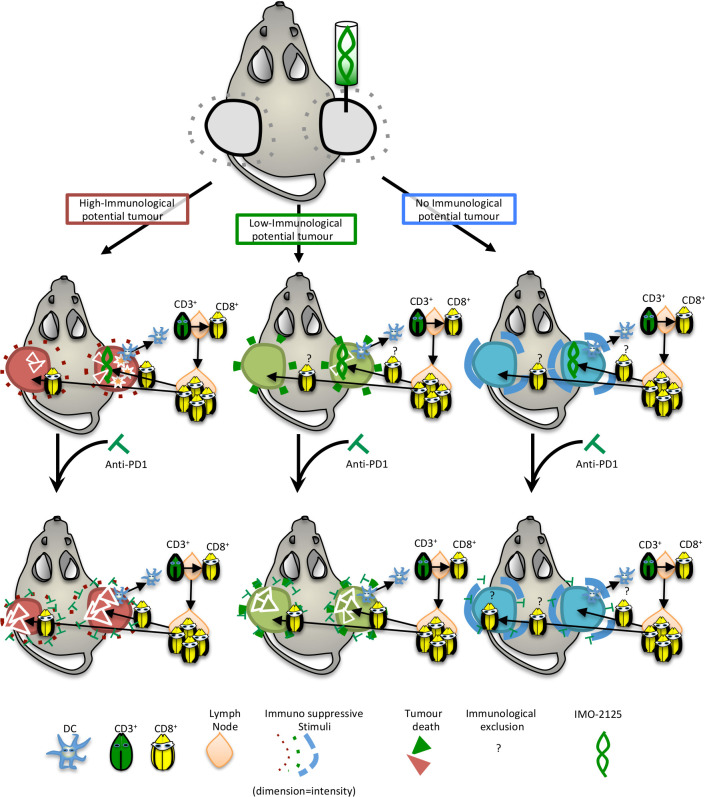
Figure 6.
Schematic representation of IMO-2125 mechanism of action. IMO-2125 (intratumoral) treatment leads to dendritic cell migration in draining lymph nodes of all pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, whereas only in the high immunological potential tumors the expression of IFNγ determines a cytokines storm that exacerbates the IMO-2125 antitumor effect. The expansion and activation of T cells in tumor-draining lymph nodes occur for all IMO-2125-treated tumors. Whereas in tumor with high immunological potential, T cells are able to efficiently kill cancer cells, tumors with low or no immunological potential are able to escape to T lymphocytes through an increase of autophagy flux and expression of immune suppressive cytokines that limited efficacy of IMO-2125. Anti-PD1 treatment is able to increase the efficacy of IMO-2125, potentiating the infiltration of T cells, only in tumor with high and low immunological potential, while no effect in the extremely refractory tumors is evident.