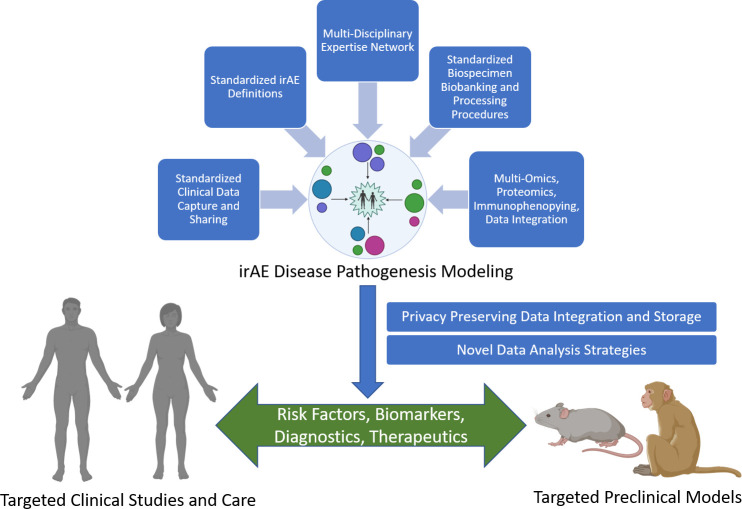
Figure 1.
Future directions for irAE research. Effective clinical modeling of irAEs will require the integration of a variety of data, including: (1) standardized definitions of irAEs and tools to identify them, (2) clinical data from electronic health records that reflect the critical components of irAEs and cancer descriptions and outcomes that have been standardized using common data models to support data sharing, (3) collaborative biospecimen biobanking programs with standardized operating procedures for tissue collection, processing and storage, and (4) high-quality, high-throughput multiomics, proteomics and immunophenotyping data integration strategies that provide mechanistic information. The overall clinical modeling of irAE disease pathogenesis efforts will require multidisciplinary clinicians and scientists and the development of modeling, management and analysis strategies and data collection from a large number of organizations to represent the wide range of irAEs, particularly rare irAEs. Clinical modeling will also require data storage technologies that support integration of clinical and mechanistic data while preserving participant privacy and novel machine learning strategies to derive insights about risk factors and biomarkers of disease that can lead to new diagnostics and therapeutics for clinical care as well as support refinement and development of more effective preclinical models. irAE, immune-related adverse event.