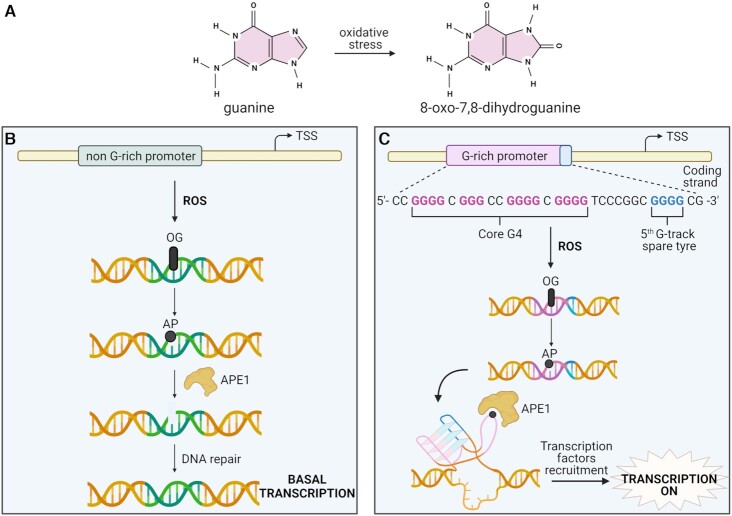
Figure 6.
G4s and DNA damage. (A) Guanine is frequently oxidized by oxidative stress generating 8-oxo-7,8-dihydroguanine (OG). (B) OG formation upon ROS damage in a gene promoter without a G4 causes the formation of an apurinic (AP) site that is recognized and cleaved by APE1. This cleaved site is subsequently repaired without increasing the gene transcription level. (C) OG formation in a gene promoter containing a core G4 sequence (in pink) and a fifth G-track (spare tyre in blue) causes the formation of an alternative G4-structure and the extrusion of the AP site into a loop. The structure is recognized and bound by APE1 which reduces the cleaving ability of APE1 and stimulates the recruitment of transcription factors with consequent transcriptional activation.