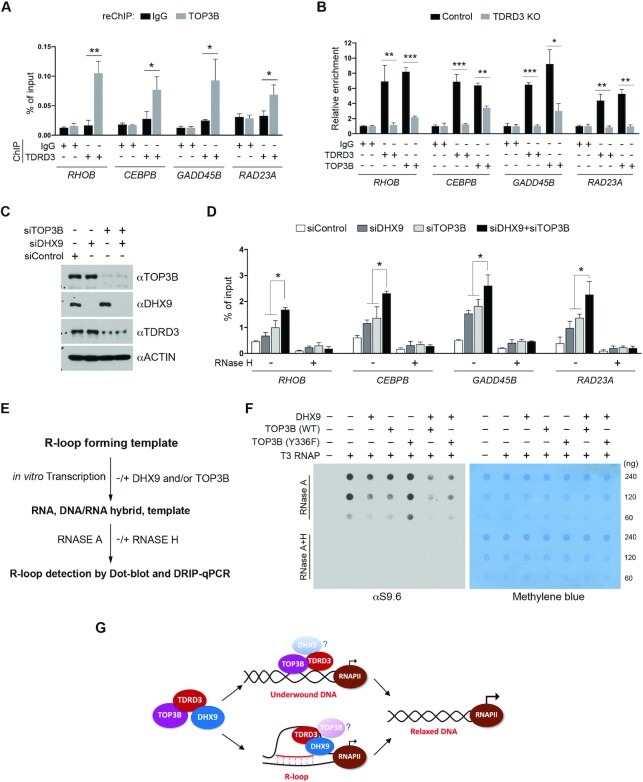
Figure 6.
DHX9 and TOP3B function together to resolve co-transcriptional R-loops. (A) A ChIP-reChIP assay was performed to detect the co-occupancy of TDRD3 and TOP3B at target gene promoters. The first round of ChIP was performed using control IgG and αTDRD3 antibodies, and the second round of ChIP (reChIP) was performed using IgG and αTOP3B antibodies. ChIP DNA was analyzed by qPCR using primers for the indicated gene promoters. (B) Loss of TDRD3 reduces TOP3B recruitment to target gene promoters. ChIP assays were performed in WT and TDRD3 KO MCF7 cells using control IgG, αTDRD3, and αTOP3B antibodies. (C) MCF7 cells were transfected with control siRNA (siControl), DHX9-specific siRNA (siDHX9), or TOP3B-specific siRNA (siTOP3B), individually or in combination. TOP3B, DHX9 and TDRD3 were detected by western blot analysis using indicated antibodies. (D) TOP3B and DHX9 function together in resolving R-loops at TDRD3 target gene promoters. DRIP-qPCR analysis was performed to compare R-loop levels at the promoters of TDRD3 target genes in control (siControl), DHX9 knockdown (siDHX9), TOP3B knockdown (siTOP3B), and DHX9/TOP3B double knockdown (siDHX9 + siTOP3B) MCF7 cells. Samples treated with RNase H served as negative controls. (E) Schematic of the in vitro plasmid-based R-loop formation assay followed by quantification of R-loop levels using Dot-blot and DRIP-qPCR. pFC53 plasmids, which contain the R-loop-forming sequence of Airn (13), were transcribed in vitro using T3 RNA polymerase under standard conditions. The transcription products, including the DNA template, the free RNA product, and R-loop containing template, were then subjected to RNase A digestion to remove RNA. The remaining samples were equally divided and either left untreated (−) or treated with RNase H (+). The final products were purified and subjected to either Dot-blot analysis or DRIP-qPCR with DNA/RNA hybrid-specific antibody (S9.6) for R-loop quantification. (F) TOP3B and DHX9 function together to resolve co-transcriptional R-loops in vitro. The pFC53 plasmid was subjected to in vitro transcription in the presence of DHX9, WT TOP3B, and topoisomerase activity-deficient (Y336F) TOP3B, either individually or in combination, as indicated. The level of R-loops in each reaction was detected by Dot-Blot using the S9.6 antibody. The loading of the nucleic acid was visualized by methylene blue staining of the membrane. (G) TDRD3 functions as a scaffold that assembles a protein complex, containing TOP3B and DHX9, to regulate co-transcriptional R-loops at gene promoters. TDRD3 not only recruits TOP3B and DHX9 to specific genomic regions, but also stimulates their respective enzymatic activities to either resolve underwound DNA to prevent R-loop formation (with TOP3B) or resolve existing R-loops to avoid R-loop accumulation (with DHX9). This activity of TDRD3 is likely conferred by its interaction with ssDNA.