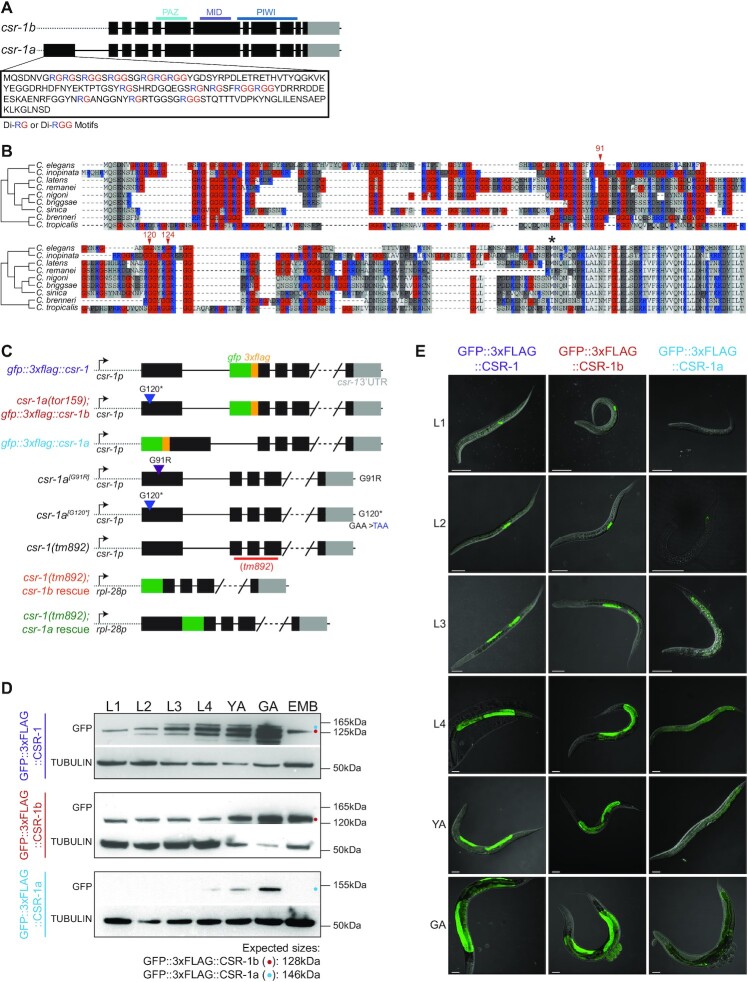
Figure 1.
CSR-1a and CSR-1b isoforms are differentially expressed throughout development. (A) Schematic representation of CSR-1 isoforms. Black boxes are exons, gray boxes are 3′UTRs. (B) Multiple sequence alignment of the N-terminal region of csr-1 for nine Caenorhabditis species. Arrows indicate C. elegans amino acid positions mutated as a result of the forward genetic screen (as shown in Supplementary Figure S1B and C). The asterisk indicates the first amino acid of CSR-1b in C. elegans. (C) Schematic representations of all csr-1 mutant strains, endogenously tagged strains and single copy transgene insertion strains used in this study. (D) Western blot using GFP antibodies to detect GFP::3xFLAG::CSR-1, GFP::3xFLAG::CSR-1b and GFP::3xFLAG::CSR-1a expression in each life stage (larval stages 1 to 4 (L1–L4), young adult (YA), gravid adult (GA) and embryo (EMB) stages). (E) Fluorescence micrographs of whole animals expressing endogenously tagged CSR-1 isoforms during each life stage (L1-L4, YA and GA). Scale bar, 50 μm.